Zimbabwe Introduces Gold Coins in Hopes of Reducing Demand for US Dollars
HARARE, ZIMBABWE —
Zimbabwe’s central bank has introduced gold coins that it hopes will ease citizens’ demands for foreign currency. But economists and ordinary Zimbabweans are skeptical.
At the official launch of the gold coins in Harare on Monday, John Mangudya, head of the Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe, said the coins are designed to reduce demand for U.S. dollars in the country.
Zimbabweans are largely shunning the weak local dollar in favor of U.S. greenbacks, which Zimbabweans see as more acceptable abroad and better at holding their value long term.
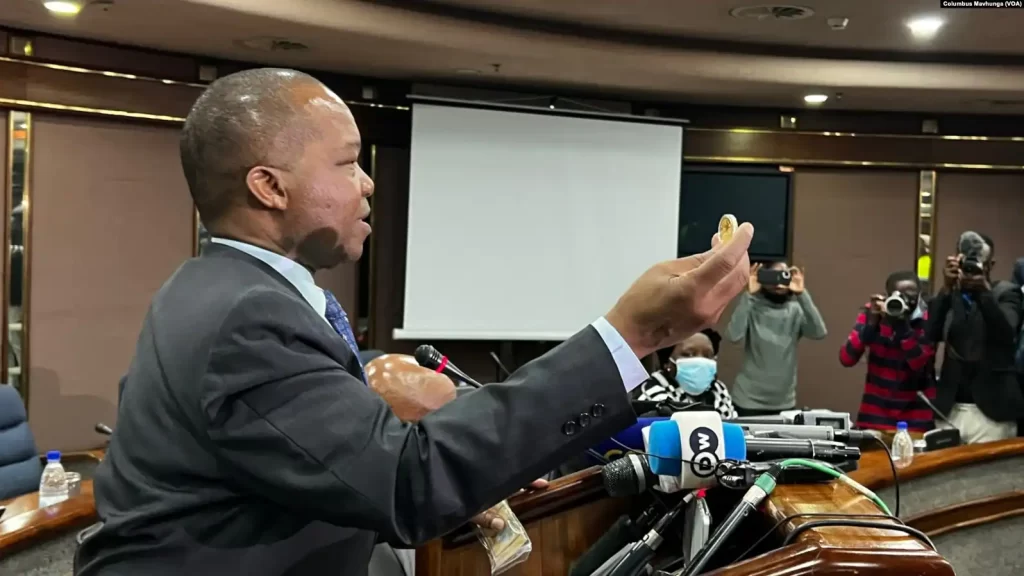

Mangudya said he hoped that Zimbabweans will now opt for the gold coins, which cost about $1,800 each.
“We are now providing that store of value to ensure that people do not run to the parallel market in search for foreign currency to store value,” he said. “And there is no other better product that can be used to store value other than gold.”
Mangudya said the coin is a sign of respect for the people of Zimbabwe.
“We know what you have been going through in terms of the fear factor of losing value and therefore we are providing this gold coin,” he said. It’s a genuine gold coin to ensure that it is saved and invested there.”
Mangudya said 2,000 coins will be manufactured, with future production depending on the public’s appetite.
Prosper Chitambara, a senior researcher and economist at the Labor and Economic Development Research Institute of Zimbabwe, said despite the bank’s hopes he doubts the coins will drastically reduce demand for American dollars.
“Even the demand for U.S. dollar as a store of value, it will also rise because there are still a lot of uncertainties relating to the convertibility of these gold coins — are [they] internationally tradeable, especially given the trust and confidence issues?” Chitambara said.

Chitambra also expressed caution about the coin.
“Most people may not have money to buy this since most citizens are literally living from hand to mouth,” Chitambara said.
One of those Zimbabweans struggling to get by is Christine Kayumba, a high school teacher in Harare.
“The issue of gold coins to us teachers in Zimbabwe, is something we can dream of,” Kayumba said. “It means a teacher who is getting a salary of $190 to $200 would need nine to 10 months to buy one gold coin.”
For Kayumba, that $200 of salary pays for transport, food, rent and money to send children to school. It’s money to live, she said, not to buy a gold coin.
“So, I believe the gold coins were meant for the rich people, not the ordinary teacher or any civil servant in Zimbabwe,” she said.
Mangudya told reporters Monday that gold coins of lesser value would be minted in future to cater for people who have fewer resources.
Government Debt to GDP in Zimbabwe
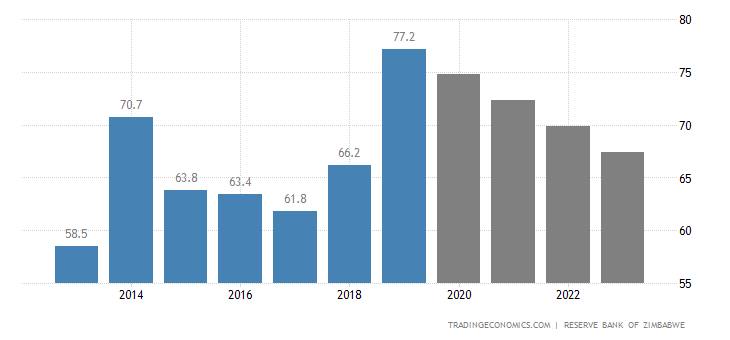
| Related | Last | Previous | Unit | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Government Debt to GDP | 77.20 | 66.20 | percent of GDP | Dec 2019 |
| Government Budget | -1.50 | -4.00 | percent of GDP | Dec 2020 |
| Actual | Previous | Highest | Lowest | Dates | Unit | Frequency | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 77.20 | 66.20 | 248.10 | 48.44 | 1990 – 2019 | percent of GDP | Yearly |

