The ‘Brandenburg test’ for incitement to violence
In 1969, the U.S. Supreme Court made history by ruling that, to merit conviction, the violence advocated must be intended, likely and imminent. By Jeff Howard.
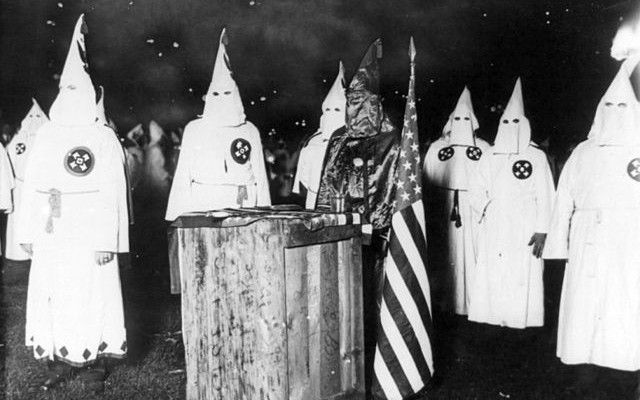

The case
Clarence Brandenburg, a 48 year-old television repair shop owner and leader of the Ku Klux Klan’s Ohio branch, held a rally in the summer of 1964 to articulate and celebrate his white supremacist ideology. Brandenburg proclaimed in front of local TV cameras: “if our president, our Congress, our Supreme Court, continues to suppress the white, Caucasian race, it’s possible that there might have to be some revengeance [sic] taken.” Indicating an impending Independence Day march on Washington, DC, the speech included such statements as, “the nigger should be returned to Africa, the Jew returned to Israel.” While Brandenburg was not evidently armed, other Klansmen at the rally were.
Interested in hate speech? More great content here:
- Too much hate? Professor Jeremy Waldron makes the case for hate speech bans
- ‘Shot the Boer’: Hate speech in the new South Africa?
- Beauty and the beast: Brigitte Bardot sanctioned for hate speech
Brandenburg was found guilty of violating Ohio state law, which prohibited “advocat[ing] . . . the duty, necessity, or propriety of crime, sabotage, violence, or unlawful methods of terrorism as a means of accomplishing industrial or political reform,” as well as “voluntarily assembl[ing] with any society, group or assemblage of persons formed to teach or advocate the doctrines of criminal syndicalism.” His penalties included a $1,000 fine and a 1-10 year prison sentence.
In a landmark judgment, the U.S. Supreme Court overturned the conviction, contending that the Ohio law affronted Brandenburg’s freedom of speech, protected by the First Amendment of the U.S. Constitution. Instead, the Court held: “Freedoms of speech and press do not permit a State to forbid advocacy of the use of force or of law violation except where such advocacy is directed to inciting or producing imminent lawless action and is likely to incite or produce such action.” Because the rally was not obviously intended to incite specific acts of violence, and because it was not likely to do so, government restriction of Brandenburg’s speech was unconstitutional.
To Learn More…. Read MORE Below and click the links
Learn More About True Threats Here below….
We also have the The Brandenburg v. Ohio (1969) – 1st Amendment
CURRENT TEST = We also have the The ‘Brandenburg test’ for incitement to violence – 1st Amendment
We also have the The Incitement to Imminent Lawless Action Test – 1st Amendment
We also have the True Threats – Virginia v. Black is most comprehensive Supreme Court definition – 1st Amendment
We also have the Watts v. United States – True Threat Test – 1st Amendment
We also have the Clear and Present Danger Test – 1st Amendment
We also have the Gravity of the Evil Test – 1st Amendment
We also have the Elonis v. United States (2015) – Threats – 1st Amendment
Learn More About What is Obscene….
We also have the Miller v. California – 3 Prong Obscenity Test (Miller Test) – 1st Amendment
We also have the Obscenity and Pornography – 1st Amendment
Learn More About Police, The Government Officials and You….
We also have the Brayshaw v. City of Tallahassee – 1st Amendment – Posting Police Address
We also have the Publius v. Boyer-Vine –1st Amendment – Posting Police Address
We also have the Lozman v. City of Riviera Beach, Florida (2018) – 1st Amendment – Retaliatory Police Arrests
We also have the Nieves v. Bartlett (2019) – 1st Amendment – Retaliatory Police Arrests
We also have the Freedom of the Press – Flyers, Newspaper, Leaflets, Peaceful Assembly – 1st Amendment
We also have the Insulting letters to politician’s home are constitutionally protected, unless they are ‘true threats’ – 1st Amendment
We also have the Introducing TEXT & EMAIL Digital Evidence in California Courts – 1st Amendment
We also have the First Amendment Encyclopedia very comprehensive – 1st Amendment
ARE PEOPLE LYING ON YOU? CAN YOU PROVE IT? IF YES…. THEN YOU ARE IN LUCK!
We also have the Penal Code 118 PC – California Penalty of “Perjury” Law
We also have the Federal Perjury – Definition by Law
We also have the Penal Code 132 PC – Offering False Evidence
We also have the Penal Code 134 PC – Preparing False Evidence
We also have the Penal Code 118.1 PC – Police Officers Filing False Reports
We also have the Spencer v. Peters – Police Fabrication of Evidence – 14th Amendment
We also have the Penal Code 148.5 PC – Making a False Police Report in California
We also have the Penal Code 115 PC – Filing a False Document in California
Know Your Rights Click Here (must read!)
Under 42 U.S.C. $ection 1983 – Recoverable Damage$
42 U.S. Code § 1983 – Civil Action for Deprivation of Right$
$ection 1983 Lawsuit – How to Bring a Civil Rights Claim
18 U.S. Code § 242 – Deprivation of Right$ Under Color of Law
18 U.S. Code § 241 – Conspiracy against Right$
$uing for Misconduct – Know More of Your Right$
Police Misconduct in California – How to Bring a Lawsuit
New Supreme Court Ruling – makes it easier to sue police
RELATIONSHIP WITH YOUR CHILDREN & YOUR CONSTITUIONAL RIGHT$ + RULING$
YOU CANNOT GET BACK TIME BUT YOU CAN HIT THOSE PUNKS WHERE THEY WILL FEEL YOU = THEIR BANK
We also have the 9.3 Section 1983 Claim Against Defendant as (Individuals) — 14th Amendment this CODE PROTECTS all US CITIZENS
We also have the Amdt5.4.5.6.2 – Parental and Children’s Rights 5th Amendment this CODE PROTECTS all US CITIZENS
We also have the 9.32 – Interference with Parent / Child Relationship – 14th Amendment this CODE PROTECTS all US CITIZENS
We also have the PARENTS RIGHTS SCOTUS RULINGS & HELP HERE for 14th Amendment PARENTS RIGHTS Help!
We also have the California Civil Code Section 52.1 Interference with exercise or enjoyment of individual rights
We also have the Parent’s Rights & Children’s Bill of Rights SCOTUS RULINGS FOR YOUR PARENT RIGHTS
Contesting / Appeal an Order / Judgment / Charge
Options to Appealing – Fighting A Judgment Without Filing An Appeal Settlement Or Mediation
Cal. Code Civ. Proc. § 1008 Motion to Reconsider
Penal Code 1385 – Dismissal of the Action for Want of Prosecution or Otherwise
Penal Code 1538.5 – Motion To Suppress Evidence in a California Criminal Case
CACI No. 1501 – Wrongful Use of Civil Proceedings
Penal Code “995 Motions” in California – Motion to Dismiss
WIC § 700.1 – If Court Grants Motion to Suppress as Evidence
 Epic Criminal / Civil Rights SCOTUS Help – Click Here
Epic Criminal / Civil Rights SCOTUS Help – Click Here
 Epic Parents SCOTUS Ruling Help– Parental Rights – Click Here
Epic Parents SCOTUS Ruling Help– Parental Rights – Click Here

