Information On Prosecutorial Discretion
A prosecuting attorney’s option to make choices with regard to charges, plea bargaining, sentence recommendation, etc.
The decision of an independent prosecutor this week not to seek criminal charges against Attorney General Edwin Meese 3d has focused new attention on the broad and controversial power granted to American prosecutors in deciding who shall be brought to justice. Far more than in any other democracy, American prosecutors have almost unfettered authority to decide whom to charge, what crimes to identify, what penalties to seek, what bail to urge, what witnesses to call, what evidence to present, what persons to give immunity from prosecution, what plea bargains to make and what sentences to negotiate.
Indeed, if a prosecutor in West Germany had uncovered as much evidence of tax and other illegalities as the independent prosecutor James C. McKay said he had, the German would have to seek charges, said Albert W. Alschuler, a professor of law at the University of Chicago. “What the American prosecutor says is more important in the outcome of a criminal case than anything else in law or the Constitution,” said Mr. Alschuler, a widely regarded expert on plea bargaining, and an opponent of it, who is the author of several law review articles on prosecutorial discretion. He added that another American prosecutor could have looked at the same facts as Mr. McKay and come up with an equally defensible decision to charge the Attorney General with felonies.
Defenders and Critics Of Prosecutorial Discretion
The discretion afforded American prosecutors is defended on the ground that it provides for case-by-case flexibility and ultimately more leniency for deserving defendants. But critics say it has been abused with considerations of race, class and political affiliation. Draft protesters, users of small amounts of marijuana and minor traffic offenders have challenged verdicts and sentences by showing that others were not prosecuted for similar crimes, and prosecutorial bias has been charged in jury selection and death penalty cases. The subject has grown so controversial in recent years that it has been the focus of more than 200 law review articles and 280 Federal court cases since 1985. That does not count the thousands of scholarly law articles, speeches and the cases in state and local courts. “It’s a fundamental topic in the criminal justice system,” said Philip B. Heymann, a professor of law at Harvard who was the Assistant United States Attorney General in charge of the criminal division from 1978 to 1981. Mr. Heymann, who heads the Center for Criminal Justice at Harvard, said prosecutors have the authority not to bring charges even when they think they can prove a crime has been committed. He noted that such decisions are necessary in part because there is so much crime in the United States; prosecutors could not possibly process all of it.
Recent Ruling by High Court Regarding Prosecutorial Discretion
In perhaps the most controversial recent case on prosecutorial discretion, the Supreme Court, in McCleskey v. Kemp, last year upheld the death penalty for a black Georgia man accused of killing a white police officer. The defense introduced a statistical analysis of 2,000 Georgia murder cases showing that prosecutors were far more likely to seek the death penalty for black murderers than whites. The Court, in a 5-to-4 vote, said the evidence of discrimination had to be clear in each individual case, not just in a statistical study. “Because discretion is essential to the criminal justice process, we would demand exceptionally clear proof before we would infer that the discretion has been abused,” the Court said.
Defenders of broad discretion say that murder, rape and armed robbery are almost always prosecuted and that individual prosecutors who misuse their powers of choice can be impeached or not re-elected. But that does not normally help defendants singled out by prosecutors in a way that may be unfair but would not be considered abusive by the courts. William F. Weld, who resigned last spring as head of the criminal division in the Justice Department, said that the Reagan Administration has concentrated on prosecuting “high-impact cases.” Those include white-collar crime and big narcotics cases. But he said there was vast variation among United States attorneys.
Prosecutorial Discretion on Cases
“Some prosecutors won’t touch a bank fraud case unless it is over $25,000,” said Mr. Weld, now a senior partner at Hale & Dorr in Washington. “Others love routine bank embezzlement cases because it fattens their conviction statistics.” Increasingly, because of changing community standards, prosecutors are seeking charges for spouse beating and date rape, charges that were rarely pursued a decade ago. In routine assault cases, charges more often are filed when the match ups of size or number are uneven than when two apparent equals have a fistfight, legal experts said. The American Civil Liberties Union has often sharply criticized what it perceives as prosecutorial abuses even while favoring the system of discretion. John Powell, the group’s legal director, said an expanding abuse involved prosecutors detaining defendants just to force confessions or unauthorized disclosures out of them.
Mr. Powell also criticized Mr. McKay, the independent prosecutor, for saying Mr. Meese was guilty of a crime but not giving the Attorney General his day in court to dispute it. Mr. Heymann of Harvard, however, said Mr. McKay’s statements were proper because he had been asked by lawmakers if crimes had been committed. Mr. Heymann added that if a prosecutor thought a suspect would try to turn a lack of prosecution into a public exoneration, a prosecutor can properly state what laws appear to have been broken. Mr. Weld said Mr. McKay appeared to have followed Federal law-enforcement guidelines in his decision not to seek charges.
The American Bar Association and Justice Department do have general standards to guide prosecutors in choosing which cases to pursue, including quality of evidence, extent of harm caused by the offense, motives of the complainant, community standards and cooperation of the accused in the apprehension of others. But some say such standards do not go far enough. Proposals include the kind of specific criteria now required of judges in sentencing, including an alleged criminal’s prior record and specific evidence of intent to commit a crime. Some critics have proposed standardized bail and allowing individual citizens more easily to sue prosecutors for abuses of discretion. “There is no requirement to treat like cases alike,” Mr. Alshuler said. He said discretion means a system that ultimately is more merciful, but that does not mean it should be so broad that “it is exercised in different ways by different people and by the same person depending on how heavy his calendar is that week.”
National District Attorneys Association puts out its standards
National Prosecution Standards – NDD can be found here
The Ethical Obligations of Prosecutors in Cases Involving Postconviction Claims of Innocence
Prosecutor’s Duty Duty to Disclose Exculpatory Evidence Fordham Law Review PDF
Chapter 14 Disclosure of Exculpatory and Impeachment Information PDF
- Police Discretion
- The police violated my rights
- DEPRIVATION OF RIGHTS UNDER COLOR OF LAW
- How to File a complaint of Police Misconduct?
- Suing for Misconduct – Know More of Your Rights
- New Supreme Court Ruling makes it easier to sue police
- Prosecutorial Misconduct, What is it?
- Frivolous, Meritless or Malicious Prosecution
- Malicious Prosecution / Prosecutorial Misconduct
- Prosecutorial Misconduct
- Vindictive Prosecution – Georgetown University
- VINDICTIVE AND SELECTIVE PROSECUTION
- Misconduct by Judges & Prosecutor
- CALIFORNIA ATTORNEY MISCONDUCT LAW
- Equality Act 2010 – Discrimination and mental health
- Motion to reconsider – Cal. Code Civ. Proc. § 1008 Section 1008
- Fighting A Judgment Without Filing An Appeal Settlement Or Mediation – Options to Appealing
- Right to Truth – Victims’ Bill of Rights – Prop 8 1982
cited http://caught.net/caught/prosecuteabuse2.htm
To Learn More…. Read MORE Below and click the links Below
Abuse & Neglect – The Mandated Reporters (Police, D.A & Medical & the Bad Actors)
Mandated Reporter Laws – Nurses, District Attorney’s, and Police should listen up
If You Would Like to Learn More About: The California Mandated Reporting LawClick Here
To Read the Penal Code § 11164-11166 – Child Abuse or Neglect Reporting Act – California Penal Code 11164-11166Article 2.5. (CANRA) Click Here
Mandated Reporter formMandated ReporterFORM SS 8572.pdf – The Child Abuse
ALL POLICE CHIEFS, SHERIFFS AND COUNTY WELFARE DEPARTMENTS INFO BULLETIN:
Click Here Officers and DA’s for (Procedure to Follow)
It Only Takes a Minute to Make a Difference in the Life of a Child learn more below
You can learn more here California Child Abuse and Neglect Reporting Law its a PDF file
Learn More About True Threats Here below….
We also have the The Brandenburg v. Ohio (1969) – 1st Amendment
CURRENT TEST = We also have the The ‘Brandenburg test’ for incitement to violence – 1st Amendment
We also have the The Incitement to Imminent Lawless Action Test– 1st Amendment
We also have the True Threats – Virginia v. Black is most comprehensive Supreme Court definition – 1st Amendment
We also have the Watts v. United States – True Threat Test – 1st Amendment
We also have the Clear and Present Danger Test – 1st Amendment
We also have the Gravity of the Evil Test – 1st Amendment
We also have the Elonis v. United States (2015) – Threats – 1st Amendment
Learn More About What is Obscene…. be careful about education it may enlighten you
We also have the Miller v. California – 3 Prong Obscenity Test (Miller Test) – 1st Amendment
We also have the Obscenity and Pornography – 1st Amendment
Learn More About Police, The Government Officials and You….
$$ Retaliatory Arrests and Prosecution $$
Anti-SLAPP Law in California
Freedom of Assembly – Peaceful Assembly – 1st Amendment Right
We also have the Brayshaw v. City of Tallahassee – 1st Amendment – Posting Police Address
We also have the Publius v. Boyer-Vine –1st Amendment – Posting Police Address
We also have the Lozman v. City of Riviera Beach, Florida (2018) – 1st Amendment – Retaliatory Police Arrests
We also have the Nieves v. Bartlett (2019) – 1st Amendment – Retaliatory Police Arrests
We also have the Hartman v. Moore (2006) – 1st Amendment – Retaliatory Police Arrests
Retaliatory Prosecution Claims Against Government Officials – 1st Amendment
We also have the Reichle v. Howards (2012) – 1st Amendment – Retaliatory Police Arrests
Retaliatory Prosecution Claims Against Government Officials – 1st Amendment
Freedom of the Press – Flyers, Newspaper, Leaflets, Peaceful Assembly – 1$t Amendment – Learn More Here
Vermont’s Top Court Weighs: Are KKK Fliers – 1st Amendment Protected Speech
We also have the Insulting letters to politician’s home are constitutionally protected, unless they are ‘true threats’ – Letters to Politicians Homes – 1st Amendment
We also have the First Amendment Encyclopedia very comprehensive – 1st Amendment
Dwayne Furlow v. Jon Belmar – Police Warrant – Immunity Fail – 4th, 5th, & 14th Amendment
ARE PEOPLE LYING ON YOU? CAN YOU PROVE IT? IF YES…. THEN YOU ARE IN LUCK!
Penal Code 118 PC – California Penalty of “Perjury” Law
Federal Perjury – Definition by Law
Penal Code 132 PC – Offering False Evidence
Penal Code 134 PC – Preparing False Evidence
Penal Code 118.1 PC – Police Officer$ Filing False Report$
Spencer v. Peters– Police Fabrication of Evidence – 14th Amendment
Penal Code 148.5 PC – Making a False Police Report in California
Penal Code 115 PC – Filing a False Document in California
Sanctions and Attorney Fee Recovery for Bad Actors
FAM § 3027.1 – Attorney’s Fees and Sanctions For False Child Abuse Allegations – Family Code 3027.1 – Click Here
FAM § 271 – Awarding Attorney Fees– Family Code 271 Family Court Sanction Click Here
Awarding Discovery Based Sanctions in Family Law Cases – Click Here
FAM § 2030 – Bringing Fairness & Fee Recovery – Click Here
Zamos v. Stroud – District Attorney Liable for Bad Faith Action – Click Here
Mi$Conduct – Pro$ecutorial Mi$Conduct
Prosecutor$
Attorney Rule$ of Engagement – Government (A.K.A. THE PRO$UCTOR) and Public/Private Attorney
What is a Fiduciary Duty; Breach of Fiduciary Duty
The Attorney’s Sworn Oath
Malicious Prosecution / Prosecutorial Misconduct – Know What it is!
New Supreme Court Ruling – makes it easier to sue police
Possible courses of action Prosecutorial Misconduct
Misconduct by Judges & Prosecutor – Rules of Professional Conduct
Functions and Duties of the Prosecutor – Prosecution Conduct
Information On Prosecutorial Discretion
Fighting Discovery Abuse in Litigation – Forensic & Investigative Accounting – Click Here
Criminal Motions § 1:9 – Motion for Recusal of Prosecutor
Pen. Code, § 1424 – Recusal of Prosecutor
Removing Corrupt Judges, Prosecutors, Jurors and other Individuals & Fake Evidence from Your Case
National District Attorneys Association puts out its standards
National Prosecution Standards – NDD can be found here
The Ethical Obligations of Prosecutors in Cases Involving Postconviction Claims of Innocence
ABA – Functions and Duties of the Prosecutor – Prosecution Conduct
Prosecutor’s Duty Duty to Disclose Exculpatory Evidence Fordham Law Review PDF
Chapter 14 Disclosure of Exculpatory and Impeachment Information PDF
Mi$Conduct – Judicial Mi$Conduct
Judge$
Prosecution Of Judges For Corrupt Practice$
Code of Conduct for United States Judge$
Disqualification of a Judge for Prejudice
Judicial Immunity from Civil and Criminal Liability
Recusal of Judge – CCP § 170.1 – Removal a Judge – How to Remove a Judge
l292 Disqualification of Judicial Officer – C.C.P. 170.6 Form
How to File a Complaint Against a Judge in California?
Commission on Judicial Performance – Judge Complaint Online Form
Why Judges, District Attorneys or Attorneys Must Sometimes Recuse Themselves
Removing Corrupt Judges, Prosecutors, Jurors and other Individuals & Fake Evidence from Your Case
Misconduct by Government Know Your Rights Click Here (must read!)
Under 42 U.S.C. $ection 1983 – Recoverable Damage$
42 U.S. Code § 1983 – Civil Action for Deprivation of Right$
18 U.S. Code § 242 – Deprivation of Right$ Under Color of Law
18 U.S. Code § 241 – Conspiracy against Right$
Section 1983 Lawsuit – How to Bring a Civil Rights Claim
Suing for Misconduct – Know More of Your Right$
Police Misconduct in California – How to Bring a Lawsuit
How to File a complaint of Police Misconduct? (Tort Claim Forms here as well)
Deprivation of Rights – Under Color of the Law
What is Sua Sponte and How is it Used in a California Court?
Removing Corrupt Judges, Prosecutors, Jurors
and other Individuals & Fake Evidence from Your Case
Anti-SLAPP Law in California
Freedom of Assembly – Peaceful Assembly – 1st Amendment Right
How to Recover “Punitive Damages” in a California Personal Injury Case
Pro Se Forms and Forms Information(Tort Claim Forms here as well)
What is Tort?
PARENT CASE LAW
RELATIONSHIP WITH YOUR CHILDREN &
YOUR CONSTITUIONAL RIGHT$ + RULING$
YOU CANNOT GET BACK TIME BUT YOU CAN HIT THOSE IMMORAL NON CIVIC MINDED PUNKS WHERE THEY WILL FEEL YOU = THEIR BANK
Family Law Appeal – Learn about appealing a Family Court Decision Here
9.3 Section 1983 Claim Against Defendant as (Individuals) —
14th Amendment this CODE PROTECT$ all US CITIZEN$
Amdt5.4.5.6.2 – Parental and Children’s Rights –
5th Amendment this CODE PROTECT$ all US CITIZEN$
9.32 – Interference with Parent / Child Relationship –
14th Amendment this CODE PROTECT$ all US CITIZEN$
California Civil Code Section 52.1
Interference with exercise or enjoyment of individual rights
Parent’s Rights & Children’s Bill of Rights
SCOTUS RULINGS FOR YOUR PARENT RIGHTS
SEARCH of our site for all articles relating for PARENTS RIGHTS Help!
Child’s Best Interest in Custody Cases
Are You From Out of State (California)? FL-105 GC-120(A)
Declaration Under Uniform Child Custody Jurisdiction and Enforcement Act (UCCJEA)
Learn More:Family Law Appeal
Necessity Defense in Criminal Cases
GRANDPARENT CASE LAW
Do Grandparents Have Visitation Rights? If there is an Established Relationship then Yes
Third “PRESUMED PARENT” Family Code 7612(C) – Requires Established Relationship Required
Cal State Bar PDF to read about Three Parent Law –
The State Bar of California family law news issue4 2017 vol. 39, no. 4.pdf
Distinguishing Request for Custody from Request for Visitation
Troxel v. Granville, 530 U.S. 57 (2000) – Grandparents – 14th Amendment
S.F. Human Servs. Agency v. Christine C. (In re Caden C.)
9.32 Particular Rights – Fourteenth Amendment – Interference with Parent / Child Relationship
Child’s Best Interest in Custody Cases
When is a Joinder in a Family Law Case Appropriate? – Reason for Joinder
Joinder In Family Law Cases – CRC Rule 5.24
GrandParents Rights To Visit
Family Law Packet OC Resource Center
Family Law Packet SB Resource Center
Motion to vacate an adverse judgment
Mandatory Joinder vs Permissive Joinder – Compulsory vs Dismissive Joinder
When is a Joinder in a Family Law Case Appropriate?
Kyle O. v. Donald R. (2000) 85 Cal.App.4th 848
Punsly v. Ho (2001) 87 Cal.App.4th 1099
Zauseta v. Zauseta (2002) 102 Cal.App.4th 1242
S.F. Human Servs. Agency v. Christine C. (In re Caden C.)
DUE PROCESS READS>>>>>>
Due Process vs Substantive Due Process learn more HERE
Understanding Due Process – This clause caused over 200 overturns in just DNA alone Click Here
Mathews v. Eldridge – Due Process – 5th & 14th Amendment Mathews Test – 3 Part Test– Amdt5.4.5.4.2 Mathews Test
“Unfriending” Evidence – 5th Amendment
At the Intersection of Technology and Law
We also have the Introducing TEXT & EMAIL Digital Evidence in California Courts – 1st Amendment
so if you are interested in learning about Introducing Digital Evidence in California State Courts
click here for SCOTUS rulings
Retrieving Evidence / Internal Investigation Case
Conviction Integrity Unit (“CIU”) of the Orange County District Attorney OCDA – Click Here
Fighting Discovery Abuse in Litigation – Forensic & Investigative Accounting – Click Here
Orange County Data, BodyCam, Police Report, Incident Reports,
and all other available known requests for data below:
APPLICATION TO EXAMINE LOCAL ARREST RECORD UNDER CPC 13321 Click Here
Learn About Policy 814: Discovery Requests OCDA Office – Click Here
Request for Proof In-Custody Form Click Here
Request for Clearance Letter Form Click Here
Application to Obtain Copy of State Summary of Criminal HistoryForm Click Here
Request Authorization Form Release of Case Information – Click Here
Texts / Emails AS EVIDENCE: Authenticating Texts for California Courts
Can I Use Text Messages in My California Divorce?
Two-Steps And Voila: How To Authenticate Text Messages
How Your Texts Can Be Used As Evidence?
California Supreme Court Rules:
Text Messages Sent on Private Government Employees Lines
Subject to Open Records Requests
case law: City of San Jose v. Superior Court – Releasing Private Text/Phone Records of Government Employees
Public Records Practices After the San Jose Decision
The Decision Briefing Merits After the San Jose Decision
CPRA Public Records Act Data Request – Click Here
Here is the Public Records Service Act Portal for all of CALIFORNIA Click Here
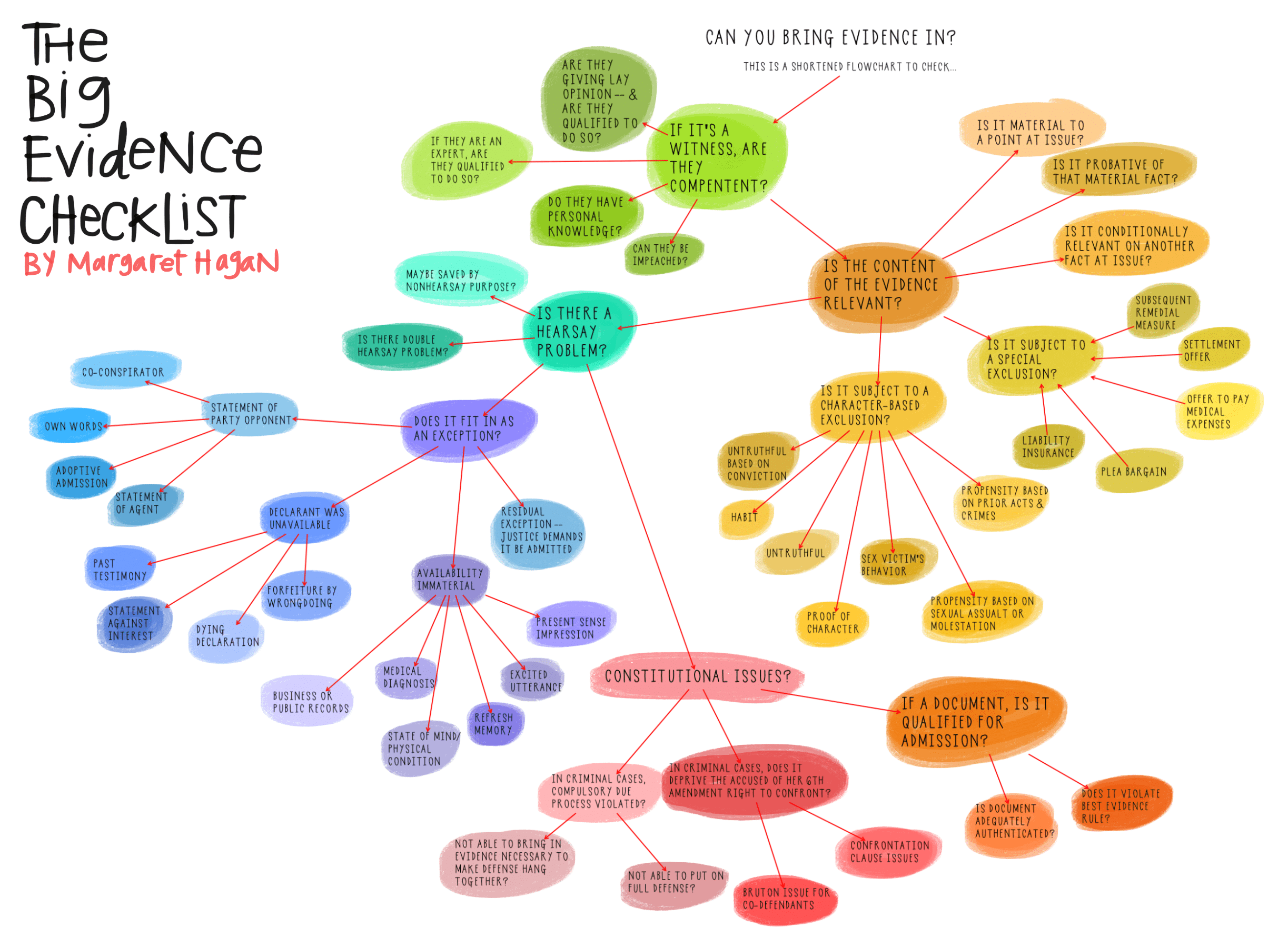
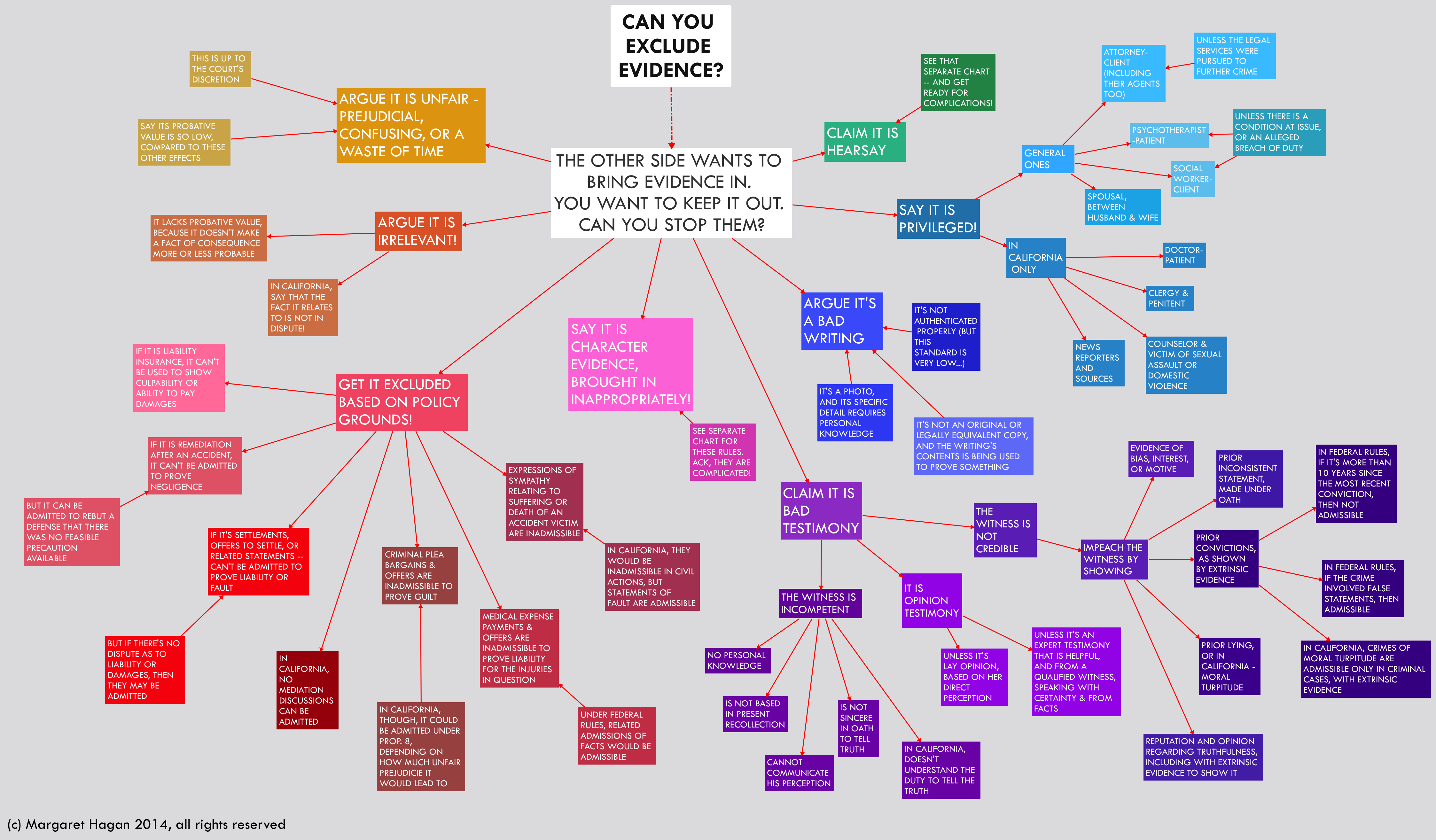
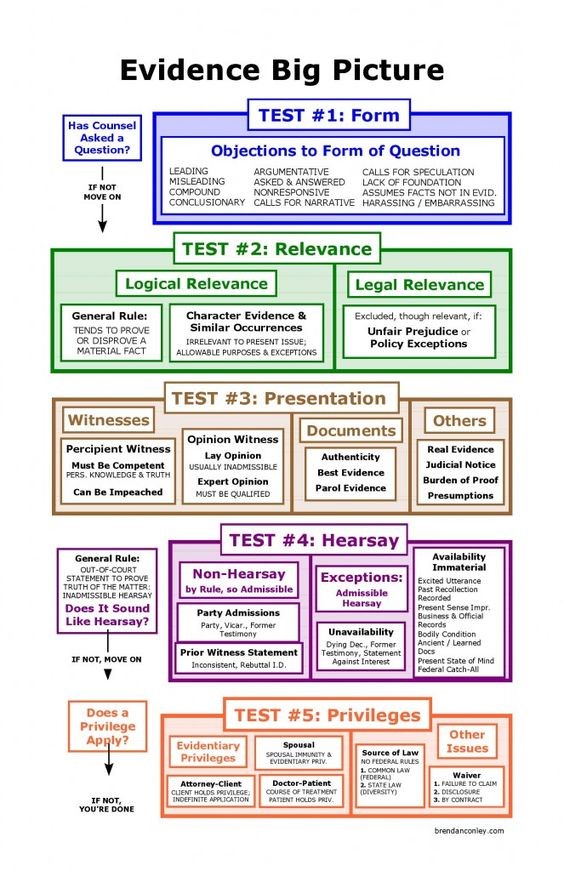
Rules of Admissibility – Evidence Admissibility
Confrontation Clause – Sixth Amendment
Exceptions To The Hearsay Rule – Confronting Evidence
Prosecutor’s Obligation to Disclose Exculpatory Evidence
Successful Brady/Napue Cases – Suppression of Evidence
Cases Remanded or Hearing Granted Based on Brady/Napue Claims
Unsuccessful But Instructive Brady/Napue Cases
ABA – Functions and Duties of the Prosecutor – Prosecution Conduct
Frivolous, Meritless or Malicious Prosecution – fiduciary duty
Appealing/Contesting Case/Order/Judgment/Charge/ Suppressing Evidence
First Things First: What Can Be Appealed and What it Takes to Get Started – Click Here
Options to Appealing– Fighting A Judgment Without Filing An Appeal Settlement Or Mediation
Cal. Code Civ. Proc. § 1008 Motion to Reconsider
Penal Code 1385 – Dismissal of the Action for Want of Prosecution or Otherwise
Penal Code 1538.5 – Motion To Suppress Evidence in a California Criminal Case
CACI No. 1501 – Wrongful Use of Civil Proceedings
Penal Code “995 Motions” in California – Motion to Dismiss
WIC § 700.1 – If Court Grants Motion to Suppress as Evidence
Suppression Of Exculpatory Evidence / Presentation Of False Or Misleading Evidence – Click Here
Notice of Appeal — Felony (Defendant) (CR-120) 1237, 1237.5, 1538.5(m) – Click Here
California Motions in Limine – What is a Motion in Limine?
Cleaning Up Your Record
Penal Code 851.8 PC – Certificate of Factual Innocence in California
Petition to Seal and Destroy Adult Arrest Records – Download the PC 851.8 BCIA 8270 Form Here
SB 393: The Consumer Arrest Record Equity Act – 851.87 – 851.92 & 1000.4 – 11105 – CARE ACT
Expungement California – How to Clear Criminal Records Under Penal Code 1203.4 PC
How to Vacate a Criminal Conviction in California – Penal Code 1473.7 PC
Seal & Destroy a Criminal Record
Cleaning Up Your Criminal Record in California (focus OC County)
Governor Pardons – What Does A Governor’s Pardon Do
How to Get a Sentence Commuted (Executive Clemency) in California
How to Reduce a Felony to a Misdemeanor – Penal Code 17b PC Motion
 Epic Criminal / Civil Right$ SCOTUS Help – Click Here
Epic Criminal / Civil Right$ SCOTUS Help – Click Here
 Epic Parents SCOTUS Ruling – Parental Right$ Help – Click Here
Epic Parents SCOTUS Ruling – Parental Right$ Help – Click Here
 Judge’s & Prosecutor’s Jurisdiction– SCOTUS RULINGS on
Judge’s & Prosecutor’s Jurisdiction– SCOTUS RULINGS on
 Prosecutional Misconduct – SCOTUS Rulings re: Prosecutors
Prosecutional Misconduct – SCOTUS Rulings re: Prosecutors
Family Treatment Court Best Practice Standards
Download Here this Recommended Citation
Please take time to learn new UPCOMING
The PROPOSED Parental Rights Amendment
to the US CONSTITUTION Click Here to visit their site
The proposed Parental Rights Amendment will specifically add parental rights in the text of the U.S. Constitution, protecting these rights for both current and future generations.
The Parental Rights Amendment is currently in the U.S. Senate, and is being introduced in the U.S. House.