California Legislature Passes Senate Bill 16; Expanding Peace Officer Records Accessible to the Public
California Senate Bill 16 (SB 16) 2023 – 2024 – Release of Records – Police officers
On September 2, 2021, the California Senate approved Senate Bill 16 (“SB 16”). Now on Governor Newsom’s desk, SB 16 reflects further efforts to increase transparency in law enforcement. In 2018, Governor Brown signed into effect legislation that significantly changed the confidential status of peace officer personnel files. SB 16 aims to expand on that change, making additional peace officer records admissible in court and accessible to the public as well as making it mandatory for agencies to review a lateral peace officer’s personnel file prior to employing that officer.
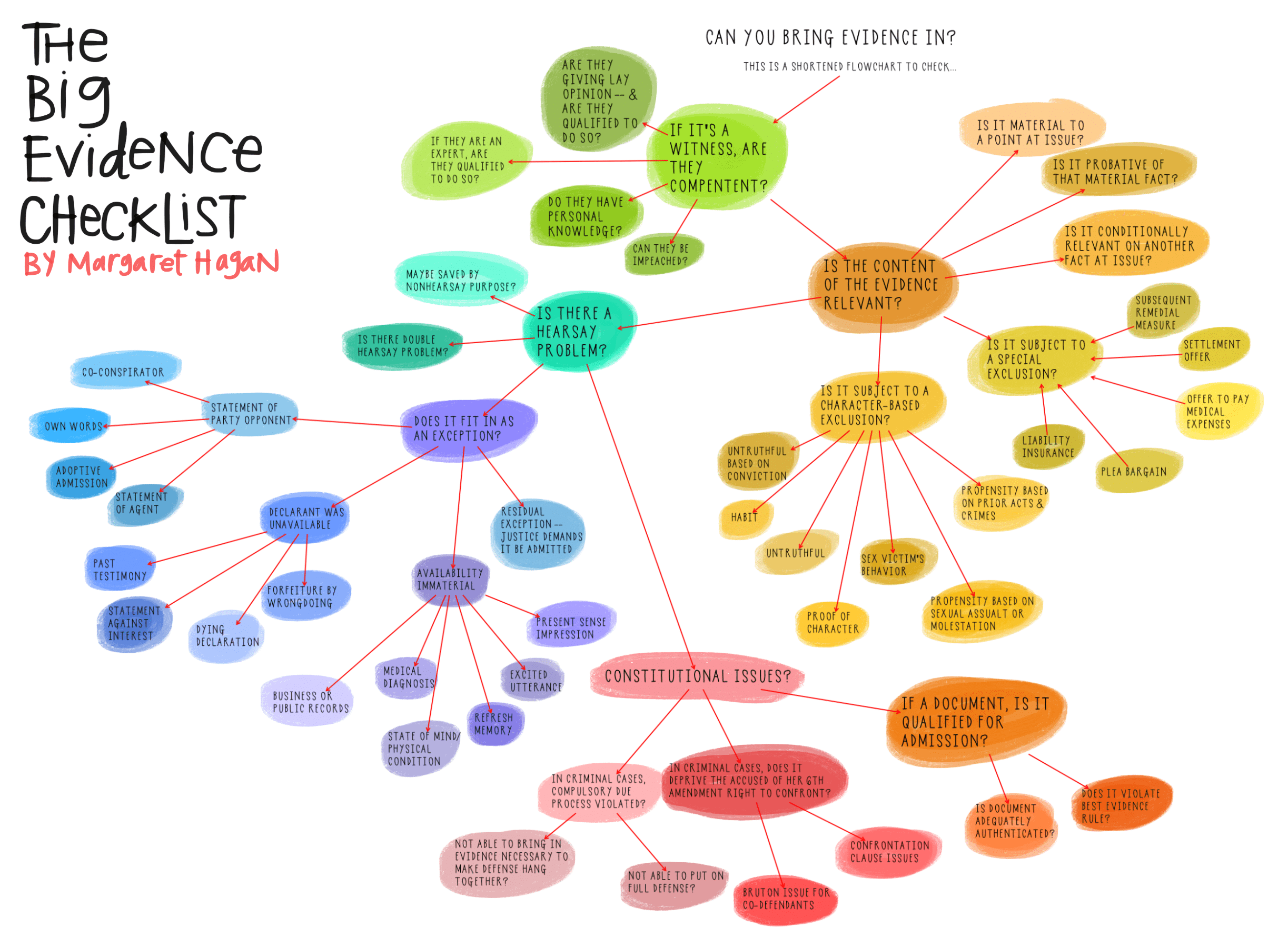
Admissibility of Peace Officer Personnel Files
Evidence Code section 1045 currently allows for relevant records of complaints, investigations of complaints, or discipline imposed related to an event in which the peace officer participated in or perceived to be admitted in court, with some exceptions. The court is required to exclude information related to complaints regarding conduct that occurred more than five years before the event that is the subject of the litigation.
SB 16 would amend Evidence Code section 1045 to remove the five year limit, allowing parties to introduce information related to complaints about conduct at any time, provided the court finds such information relevant to the matter at hand.
Accessibility of Peace Officer Personnel Files
In 2018, Governor Brown signed into effect sweeping changes to public access to peace officer personnel files. SB 16 would expand the categories of records accessible to the public pursuant to a California Public Records Act (“CPRA”) request to include records related to the following:
- Sustained findings involving complaints of unreasonable or excessive force
- Sustained findings that a peace officer failed to intervene against another officer using clearly unreasonable or excessive force
- Sustained findings of conduct involving prejudice or discrimination based on a protected classification (e.g. race, age, sex)
- Sustained findings of unlawful arrest or unlawful search
SB 16 would further expand the scope of accessible records by increasing the required record retention period from five to fifteen years where misconduct is sustained, and require the release of records for peace officers who resigned prior to the close of the investigation into their conduct.
SB 16 would also amend Penal Code section 832.7 to require law enforcement agencies to release records pursuant to a CPRA request within forty-five (45) days of the request, except as authorized by the section. Currently, there is no time limit to provide responsive records.
Law Enforcement Agency Review of Records
SB 16 would amend Penal Code section 832.12 making it mandatory for a law enforcement agency to request and review any record of investigation from a previous employing agency involving the lateral officer prior to employing that peace officer.
Conclusion
SB 16 reflects a further push to increase transparency in law enforcement, buoyed by the events that took place in the summer of 2020. Should SB 16 be signed into effect, law enforcement agencies must ensure their record retention policies and procedure for responding to CPRA requests comport with redefined scope of accessible records. Our office will continue to monitor SB 16 and provide updates on the status of the bill.
New Law Expands Public Access to Police Misconduct Records
SB 16 Signed Into Law by Gov. Gavin Newsom on September 30
California’s governor signed a package of public safety measures today, including SB 16, which clarifies and expands on the law requiring the disclosure of police records. The new law provides agencies with more specific guidance on how and when to disclose police personnel records.
The procedural changes to the law—like timing for disclosure and mandating certain retention periods—go into effect in 2022. More substantive changes—including expanding the scope of disclosures required by adding four new categories of records for release—will not be implemented until 2023. This delayed enactment gives local agencies a year to prepare for the disclosure of the backlog of police records that will surely be requested in light of this new law. A flurry of litigation may also ensue and disputes over the law’s application will garner substantial public interest.
As discussed in detail here, SB 16 will require disclosure when there is:
- a sustained finding involving a complaint that alleges unreasonable or excessive force;
- a sustained finding that an officer failed to intervene against another officer using force that is clearly unreasonable or excessive;
- a sustained finding made by any law enforcement agency or oversight agency that a peace officer or custodial officer engaged in conduct including, but not limited to, verbal statements, writings, online posts, recordings and gestures involving prejudice or discrimination against a person on the basis of race, religious creed, color, national origin, ancestry, physical disability, mental disability, medical condition, genetic information, marital status, sex, gender, gender identity, gender expression, age, sexual orientation, or military and veteran status; or
- a sustained finding made by any law enforcement agency or oversight agency that the peace officer made an unlawful arrest or conducted an unlawful search.
The California Legislature approved Sen. Nancy Skinner’s Senate Bill 16 on September 2, putting the question of whether to require disclosure of more police records before Gov. Gavin Newsom. He must sign or veto the bill by October 10.
SB 16, which builds on the landmark SB 1421, greatly expands the types of police records that must be disclosed, adding four categories to the four existing disclosure mandates. SB 16 would require disclosure when there is:
- a sustained finding involving a complaint that alleges unreasonable or excessive force;
- a sustained finding that an officer failed to intervene against another officer using force that is clearly unreasonable or excessive;
- a sustained finding made by any law enforcement agency or oversight agency that a peace officer or custodial officer engaged in conduct including, but not limited to, verbal statements, writings, online posts, recordings and gestures involving prejudice or discrimination against a person on the basis of race, religious creed, color, national origin, ancestry, physical disability, mental disability, medical condition, genetic information, marital status, sex, gender, gender identity, gender expression, age, sexual orientation, or military and veteran status; or
- a sustained finding made by any law enforcement agency or oversight agency that the peace officer made an unlawful arrest or conducted an unlawful search.
Bill Expanding Public Access to Police Misconduct Records Approved by California Senate
Gov. Gavin Newsom Must Sign or Veto by October 10
The bill delays implementation for all four new categories, giving agencies until January 2023 before they must produce these newly accessible records.
These additional notable provisions of the bill, discussed below, will go into effect Jan. 1, 2022 if the measure is signed:
- Records with no sustained finding of misconduct must be retained for at least 5 years and records related to sustained misconduct must be retained for a minimum of 15 years.
- Records relating to an incomplete investigation must be released if an officer resigned during the investigation.
- Whistleblowers and victims are added to the list of persons whose identities are required to remain confidential.
- Records shall be provided at the “earliest possible time” and “no later than 45 days from the date of a request for their disclosure” unless the law specifically permits a longer response time.
- An agency may only charge the direct cost of duplication for the production of these records, in line with the Public Records Act, and not for searching or redacting records.
- Attorney-client privilege does not prohibit the disclosure of factual information provided by the public entity to its attorney or factual information discovered in any investigation conducted by, or on behalf of, the public entity’s attorney; nor does it prohibit disclosure of billing records related to the work done by the attorney so long as the records do not relate to active and ongoing litigation and do not disclose information for the purpose of legal consultation between the public entity and its attorney.
- A public agency hiring a peace officer must review any files that must be disclosed by section 832.7 before hiring the officer.
If the governor approves SB 16, law enforcement agencies will face additional work to produce more police records and police personnel files. Every California law enforcement agency can expect to receive requests for each new category of disclosure if this law goes into effect. As with the passage of SB 1421, a flurry of litigation may also ensue and disputes over the law’s application will garner substantial public interest.
Disclaimer: BB&K Legal Alerts are not intended as legal advice. Additional facts, facts specific to your situation or future developments may affect subjects contained herein. Seek the advice of an attorney before acting or relying upon any information herein.
- (a) This article does not affect the right of access to records of complaints, or investigations of complaints, or discipline imposed as a result of those investigations, concerning an event or transaction in which the peace officer or custodial officer, as defined in Section 831.5 of the Penal Code, participated, or which the officer perceived, and pertaining to the manner in which the officer performed the officer’s duties, provided that information is relevant to the subject matter involved in the pending litigation.
- (b) In determining relevance, the court shall examine the information in chambers in conformity with Section 915, and shall exclude from disclosure both of the following:
- (1) In any criminal proceeding the conclusions of any officer investigating a complaint filed pursuant to Section 832.5 of the Penal Code.
- (2) Facts sought to be disclosed that are so remote as to make disclosure of little or no practical benefit.
- (c) In determining relevance where the issue in litigation concerns the policies or pattern of conduct of the employing agency, the court shall consider whether the information sought may be obtained from other records maintained by the employing agency in the regular course of agency business which would not necessitate the disclosure of individual personnel records.
- (d) Upon motion seasonably made by the governmental agency which has custody or control of the records to be examined or by the officer whose records are sought, and upon good cause showing the necessity thereof, the court may make any order which justice requires to protect the officer or agency from unnecessary annoyance, embarrassment or oppression.
- (e) The court shall, in any case or proceeding permitting the disclosure or discovery of any peace or custodial officer records requested pursuant to Section 1043, order that the records disclosed or discovered may not be used for any purpose other than a court proceeding pursuant to applicable law.
- (a)
- (1) Each department or agency in this state that employs peace officers shall establish a procedure to investigate complaints by members of the public against the personnel of these departments or agencies, and shall make a written description of the procedure available to the public.
- (2) Each department or agency that employs custodial officers, as defined in Section 831.5, may establish a procedure to investigate complaints by members of the public against those custodial officers employed by these departments or agencies, provided however, that any procedure so established shall comply with the provisions of this section and with the provisions of Penal Code 832.7.
- (b) Complaints and any reports or findings relating to these complaints, including all complaints and any reports currently in the possession of the department or agency, shall be retained for a period of no less than 5 years for records where there was not a sustained finding of misconduct and for not less than 15 years where there was a sustained finding of misconduct. A record shall not be destroyed while a request related to that record is being processed or any process or litigation to determine whether the record is subject to release is ongoing. All complaints retained pursuant to this subdivision may be maintained either in the peace or custodial officer’s general personnel file or in a separate file designated by the department or agency as provided by department or agency policy, in accordance with all applicable requirements of law. However, prior to any official determination regarding promotion, transfer, or disciplinary action by an officer’s employing department or agency, the complaints described by subdivision
- (c) shall be removed from the officer’s general personnel file and placed in a separate file designated by the department or agency, in accordance with all applicable requirements of law.
- (c) Complaints by members of the public that are determined by the peace or custodial officer’s employing agency to be frivolous, as defined in Section 128.5 of the Code of Civil Procedure, or unfounded or exonerated, or any portion of a complaint that is determined to be frivolous, unfounded, or exonerated, shall not be maintained in that officer’s general personnel file. However, these complaints shall be retained in other, separate files that shall be deemed personnel records for purposes of the California Public Records Act (Chapter 3.5 (commencing with Section 6250) of Division 7 of Title 1 of the Government Code) and Section 1043 of the Evidence Code.
- (1) Management of the peace or custodial officer’s employing agency shall have access to the files described in this subdivision.
- (2) Management of the peace or custodial officer’s employing agency shall not use the complaints contained in these separate files for punitive or promotional purposes except as permitted by subdivision (f) of Section 3304 of the Government Code.
- (3) Management of the peace or custodial officer’s employing agency may identify any officer who is subject to the complaints maintained in these files which require counseling or additional training. However, if a complaint is removed from the officer’s personnel file, any reference in the personnel file to the complaint or to a separate file shall be deleted.
- (d) As used in this section, the following definitions apply:
- (1) “General personnel file” means the file maintained by the agency containing the primary records specific to each peace or custodial officer’s employment, including evaluations, assignments, status changes, and imposed discipline.
- (2) “Unfounded” means that the investigation clearly established that the allegation is not true.
- (3) “Exonerated” means that the investigation clearly established that the actions of the peace or custodial officer that formed the basis for the complaint are not violations of law or department policy.
- (a) Except as provided in subdivision (b), the personnel records of peace officers and custodial officers and records maintained by a state or local agency pursuant to Section 832.5, or information obtained from these records, are confidential and shall not be disclosed in any criminal or civil proceeding except by discovery pursuant to Sections 1043 and 1046 of the Evidence Code. This section does not apply to investigations or proceedings concerning the conduct of peace officers or custodial officers, or an agency or department that employs those officers, conducted by a grand jury, a district attorney’s office, or the Attorney General’s office.
- (b) (1) Notwithstanding subdivision (a), subdivision (f) of Section 6254 of the Government Code, or any other law, the following peace officer or custodial officer personnel records and records maintained by a state or local agency shall not be confidential and shall be made available for public inspection pursuant to the California Public Records Act (Chapter 3.5 (commencing with Section 6250) of Division 7 of Title 1 of the Government Code)
-
- (A) A record relating to the report, investigation, or findings of any of the following:
- (i) An incident involving the discharge of a firearm at a person by a peace officer or custodial officer.
- (ii) An incident involving the use of force against a person by a peace officer or custodial officer that resulted in death or in great bodily injury.
- (iii) A sustained finding involving a complaint that alleges unreasonableor excessive force.
- (iv) A sustained finding that an officer failed to intervene against another officer using force that is clearly unreasonable or excessive.
- (B)
- (i) Any record relating to an incident in which a sustained finding was made by any law enforcement agency or oversight agency that a peace officer or custodial officer engaged in sexual assault involving a member of the public.
- (ii) As used in this subparagraph, “sexual assault” means the commission or attempted initiation of a sexual act with a member of the public by means of force, threat, coercion, extortion, offer of leniency or other official favor, or under the color of authority. For purposes of this definition, the propositioning for or commission of any sexual act while on duty is considered a sexual assault.
- (iii) As used in this subparagraph, “member of the public” means any person not employed by the officer’s employing agency and includes any participant in a cadet, explorer, or other youth program affiliated with the agency.
- (C) Any record relating to an incident in which a sustained finding was made by any law enforcement agency or oversight agency involving dishonesty by a peace officer or custodial officer directly relating to the reporting, investigation, or prosecution of a crime, or directly relating to the reporting of, or investigation of misconduct by, another peace officer or custodial officer, including, but not limited to, any false statements, filing false reports, destruction, falsifying, or concealing of evidence, or perjury.
- (D) Any record relating to an incident in which a sustained finding was made by any law enforcement agency or oversight agency that a peace officer or custodial officer engaged in conduct including, but not limited to, verbal statements, writings, online posts, recordings, and gestures, involving prejudice or discrimination against a person on the basis of race, religious creed, color, national origin, ancestry, physical disability, mental disability, medical condition, genetic information, marital status, sex, gender, gender identity, gender expression, age, sexual orientation, or military and veteran status.
- (E) Any record relating to an incident in which a sustained finding was made by any law enforcement agency or oversight agency that the peace officer made an unlawful arrest or conducted an unlawful search.
- (2) Records that are subject to disclosure under clause (iii) or (iv) of subparagraph (A) of paragraph (1), or under subparagraph (D) or (E) of paragraph (1), relating to an incident that occurred before January 1, 2022, shall not be subject to the time limitations in paragraph (8) until January 1, 2023.
- (3) Records that shall be released pursuant to this subdivision include all investigative reports; photographic, audio, and video evidence; transcripts or recordings of interviews; autopsy reports; all materials compiled and presented for review to the district attorney or to any person or body charged with determining whether to file criminal charges against an officer in connection with an incident, whether the officer’s action was consistent with law and agency policy for purposes of discipline or administrative action, or what discipline to impose or corrective action to take; documents setting forth findings or recommended findings; and copies of disciplinary records relating to the incident, including any letters of intent to impose discipline, any documents reflecting modifications of discipline due to the Skelly or grievance process, and letters indicating final imposition of discipline or other documentation reflecting implementation of corrective action. Records that shall be released pursuant to this subdivision also include records relating to an incident specified in paragraph (1) in which the peace officer or custodial officer resigned before the law enforcement agency or oversight agency concluded its investigation into the alleged incident.
- (4) A record from a separate and prior investigation or assessment of a separate incident shall not be released unless it is independently subject to disclosure pursuant to this subdivision.
- (5) If an investigation or incident involves multiple officers, information about allegations of misconduct by, or the analysis or disposition of an investigation of, an officer shall not be released pursuant to subparagraph (B), (C), (D), or (E) of paragraph (1), unless it relates to a sustained finding regarding that officer that is itself subject to disclosure pursuant to this section. However, factual information about that action of an officer duringan incident, or the statements of an officer about an incident, shall be released if they are relevant to a finding against another officer that is subject to release pursuant to subparagraph (B), (C), (D), or (E) of paragraph (1).
- (6) An agency shall redact a record disclosed pursuant to this section only for any of the following purposes: (A) To remove personal data or information, such as a home address, telephone number, or identities of family members, other than the names and work-related information of peace and custodial officers. (B) To preserve the anonymity of whistleblowers, complainants, victims, and witnesses. (C) To protect confidential medical, financial, or other information of which disclosure is specifically prohibited by federal law or would cause an unwarranted invasion of personal privacy that clearly outweighs the strong public interest in records about possible misconduct and use of force by peace officers and custodial officers. (D) Where there is a specific, articulable, and particularized reason to believe that disclosure of the record would pose a significant danger to the physical safety of the peace officer, custodial officer, or another person.
- (7) Notwithstanding paragraph (6), an agency may redact a record disclosed pursuant to this section, including personal identifying information, where, on the facts of the particular case, the public interest served by not disclosing the information clearly outweighs the public interest served by disclosure of the information.
- (8) An agency may withhold a record of an incident described in paragraph (1) that is the subject of an active criminal or administrative investigation, in accordance with any of the following:
- (A)
- (i) During an active criminal investigation, disclosure may be delayed for up to 60 days from the date the misconduct or use of force occurred or until the district attorney determines whether to file criminal charges related to the misconduct or use of force, whichever occurs sooner. If an agency delays disclosure pursuant to this clause, the agency shall provide, in writing, the specific basis for the agency’s determination that the interest in delaying disclosure clearly outweighs the public interest in disclosure. This writing shall include the estimated date for disclosure of the withheld information.
- (ii) After 60 days from the misconduct or use of force, the agency may continue to delay the disclosure of records or information if the disclosure could reasonably be expected to interfere with a criminal enforcement proceeding against an officer who engaged in misconduct or used the force. If an agency delays disclosure pursuant to this clause, the agency shall, at 180-day intervals as necessary, provide, in writing, the specific basis for the agency’s determination that disclosure could reasonably be expected to interfere with a criminal enforcement proceeding. The writing shall include the estimated date for the disclosure of the withheld information. Information withheld by the agency shall be disclosed when the specific basis for withholding is resolved, when the investigation or proceeding is no longer active, or by no later than 18 months after the date of the incident, whichever occurs sooner.
- (iii) After 60 days from the misconduct or use of force, the agency may continue to delay the disclosure of records or information if the disclosure could reasonably be expected to interfere with a criminal enforcement proceeding against someone other than the officer who engaged in the misconduct or used the force. If an agency delays disclosure under this clause, the agency shall, at 180-day intervals, provide, in writing, the specific basis why disclosure could reasonably be expected to interfere with a criminal enforcement proceeding, and shall provide an estimated date for the disclosure of the withheld information. Information withheld by the agency shall be disclosed when the specific basis for withholding is resolved, when the investigation or proceeding is no longer active, or by no later than 18 months after the date of the incident, whichever occurs sooner, unless extraordinary circumstances warrant continued delay due to the ongoing criminal investigation or proceeding. In that case, the agency must show by clear and convincing evidence that the interest in preventing prejudice to the active and ongoing criminal investigation or proceeding outweighs the public interest in prompt disclosure of records about misconduct or use of force by peace officers and custodial officers. The agency shall release all information subject to disclosure that does not cause substantial prejudice, including any documents that have otherwise become available.
- (iv) In an action to compel disclosure brought pursuant to Section 6258 of the Government Code, an agency may justify delay by filing an application to seal the basis for withholding, in accordance with Rule 2.550 of the California Rules of Court, or any successor rule, if disclosure of the written basis itself would impact a privilege or compromise a pending investigation. (B) If criminal charges are filed related to the incident in which misconduct occurred or force was used, the agency may delay the disclosure of records or information until a verdict on those charges is returned at trial or, if a plea of guilty or no contest is entered, the time to withdraw the plea pursuant to Section 1018. (C) During an administrative investigation into an incident described in paragraph (1), the agency may delay the disclosure of records or information until the investigating agency determines whether the misconduct or use of force violated a law or agency policy, but no longer than 180 days after the date of the employing agency’s discovery of the misconduct or use of force, or allegation of misconduct or use of force, by a person authorized to initiate an investigation.
- (A)
- (9) A record of a complaint, or the investigations, findings, or dispositions of that complaint, shall not be released pursuant to this section if the complaint is frivolous, as defined in Section 128.5 of the Code of Civil Procedure, or if the complaint is unfounded.
- (10) The cost of copies of records subject to disclosure pursuant to this subdivision that are made available upon the payment of fees covering direct costs of duplication pursuant to subdivision (b) of Section 6253 of the Government Code shall not include the costs of searching for, editing, or redacting the records.
- (11) Except to the extent temporary withholding for a longer period is permitted pursuant to paragraph (8), records subject to disclosure under this subdivision shall be provided at the earliest possible time and no later than 45 days from the date of a request for their disclosure.
- (12)
- (A) For purposes of releasing records pursuant to this subdivision, the lawyer-client privilege does not prohibit the disclosure of either of the following:
- (i) Factual information provided by the public entity to its attorney or factual information discovered in any investigation conducted by, or on behalf of, the public entity’s attorney.
- (ii) Billing records related to the work done by the attorney so long as the records do not relate to active and ongoing litigation and do not disclose information for the purpose of legal consultation between the public entity and its attorney.
- (B) This paragraph does not prohibit the public entity from asserting that a record or information within the record is exempted or prohibited from disclosure pursuant to any other federal or state law.
- (A) For purposes of releasing records pursuant to this subdivision, the lawyer-client privilege does not prohibit the disclosure of either of the following:
- (A) A record relating to the report, investigation, or findings of any of the following:
- (c) Notwithstanding subdivisions (a) and (b), a department or agency shall release to the complaining party a copy of the complaining party’s own statements at the time the complaint is filed.
- (d) Notwithstanding subdivisions (a) and (b), a department or agency that employs peace or custodial officers may disseminate data regarding the number, type, or disposition of complaints (sustained, not sustained, exonerated, or unfounded) made against its officers if that information is in a form which does not identify the individuals involved.
- (e) Notwithstanding subdivisions (a) and (b), a department or agency that employs peace or custodial officers may release factual information concerning a disciplinary investigation if the officer who is the subject of the disciplinary investigation, or the officer’s agent or representative, publicly makes a statement they know to be false concerning the investigation or the imposition of disciplinary action. Information may not be disclosed by the peace or custodial officer’s employer unless the false statement was published by an established medium of communication, such as television, radio, or a newspaper. Disclosure of factual information by the employing agency pursuant to this subdivision is limited to facts contained in the officer’s personnel file concerning the disciplinary investigation or imposition of disciplinary action that specifically refute the false statements made public by the peace or custodial officer or their agent or representative.
- (f)
- (1) The department or agency shall provide written notification to the complaining party of the disposition of the complaint within 30 days of the disposition.
- (2) The notification described in this subdivision is not conclusive or binding or admissible as evidence in any separate or subsequent action or proceeding brought before an arbitrator, court, or judge of this state or the United States.
- (g) This section does not affect the discovery or disclosure of information contained in a peace or custodial officer’s personnel file pursuant to Section 1043 of the Evidence Code.
- (h) This section does not supersede or affect the criminal discovery process outlined in Chapter 10 (commencing with Section 1054) of Title 6 of Part 2, or the admissibility of personnel records pursuant to subdivision
- (a), which codifies the court decision in Pitchess v. Superior Court (1974) 11 Cal.3d 531.
- (i) Nothing in this chapter is intended to limit the public’s right of access as provided for in Long Beach Police Officers Association v. City of Long Beach (2014) 59 Cal.4th 59.
- (a) Each department or agency in this state that employs peace officers shall make a record of any investigations of misconduct involving a peace officer in the officer’s general personnel file or a separate file designated by the department or agency. A peace officer seeking employment with a department or agency in this state that employs peace officers shall give written permission for the hiring department or agency to view the officer’s general personnel file and any separate file designated by a department or agency.
- (b) Prior to employing any peace officer, each department or agency in this state that employs peace officers shall request, and the hiring department or agency shall review, any records made available pursuant to subdivision (a).
More access also below
Section 832.7 – Peace officer or custodial officer personnel records
Senate Bill No. 1421 – California Public Records Act
Assembly Bill 748 Makes Video Evidence Captured by Police Agencies Subject to Disclosure as Public Records
SB 2, Creating Police Decertification Process and Expanding Civil Liability Exposure
California Senate Bill 16 (SB 16) – 2023-2024 – Peace officers: Release of Records
The Right To Know: How To Fulfill The Public’s Right Of Access To Police Records
PUBLIC RECORDS REQUEST CONTACTS for Los Angeles County (click here for media policy)
How Access to California Police Records
Los Angeles County Sheriff’s Department SB-1421 Records
Obtaining a Report from LASD Records (You, 3rd party or consel can obtain)
SEARCH SB-1421 SB-16 Incidents of LA County, Oakland
SB1421 – Form Access to California Police Records
California Statewide CPRA Requests Submit a CPRA Request
How do I submit a request for information?
To submit a request send the request via mail, fax, or email to the agency. Some agencies list specific departments or people whose job it is to respond to PRA requests, so check their websites or call them for further info. Always keep a copy of your request so that you can show what you submitted and when.
from the ACLU we have 2 types of SB 1421 Templates for Sample Requests
1. Incident Based Request: Use this template if you want records related to a particular incident, like the investigative record for a specific police shooting, an arrest where you believe an officer may have been found to have filed a false report, or to find out whether complaint that an officer committed sexual assault was sustained.
ACLU Download Word document | ACLU Download PDF
or from us Download Word document | or from us Download PDF
2. Officer Based Request: Use this template if you want to find any public records of misconduct related to a particular officer or if he or she has been involved in past serious uses of force.
ACLU Download Word document | ACLU Download PDF
or from us Download Word document | or from us Download PDF
We also have more robust sample letters below:
Sample Letter | SB 1421 & SB 16 Records
Download Word document | Download PDF
Sample Letter | Police Recordings
Download Word document | Download PDF
The CPRA is now located at Government Code sections 7920.000-7931.000
The First Amendment Coalition also has some useful information to help explain the PRA process.
To Learn More…. Read MORE Below and click the links Below
Abuse & Neglect – The Mandated Reporters (Police, D.A & Medical & the Bad Actors)
Mandated Reporter Laws – Nurses, District Attorney’s, and Police should listen up
If You Would Like to Learn More About: The California Mandated Reporting LawClick Here
To Read the Penal Code § 11164-11166 – Child Abuse or Neglect Reporting Act – California Penal Code 11164-11166Article 2.5. (CANRA) Click Here
Mandated Reporter formMandated ReporterFORM SS 8572.pdf – The Child Abuse
ALL POLICE CHIEFS, SHERIFFS AND COUNTY WELFARE DEPARTMENTS INFO BULLETIN:
Click Here Officers and DA’s for (Procedure to Follow)
It Only Takes a Minute to Make a Difference in the Life of a Child learn more below
You can learn more here California Child Abuse and Neglect Reporting Law its a PDF file
Learn More About True Threats Here below….
We also have the The Brandenburg v. Ohio (1969) – 1st Amendment
CURRENT TEST = We also have the The ‘Brandenburg test’ for incitement to violence – 1st Amendment
We also have the The Incitement to Imminent Lawless Action Test– 1st Amendment
We also have the True Threats – Virginia v. Black is most comprehensive Supreme Court definition – 1st Amendment
We also have the Watts v. United States – True Threat Test – 1st Amendment
We also have the Clear and Present Danger Test – 1st Amendment
We also have the Gravity of the Evil Test – 1st Amendment
We also have the Elonis v. United States (2015) – Threats – 1st Amendment
Learn More About What is Obscene…. be careful about education it may enlighten you
We also have the Miller v. California – 3 Prong Obscenity Test (Miller Test) – 1st Amendment
We also have the Obscenity and Pornography – 1st Amendment
Learn More About Police, The Government Officials and You….
$$ Retaliatory Arrests and Prosecution $$
Anti-SLAPP Law in California
Freedom of Assembly – Peaceful Assembly – 1st Amendment Right
Supreme Court sets higher bar for prosecuting threats under First Amendment 2023 SCOTUS
We also have the Brayshaw v. City of Tallahassee – 1st Amendment – Posting Police Address
We also have the Publius v. Boyer-Vine –1st Amendment – Posting Police Address
We also have the Lozman v. City of Riviera Beach, Florida (2018) – 1st Amendment – Retaliatory Police Arrests
We also have the Nieves v. Bartlett (2019) – 1st Amendment – Retaliatory Police Arrests
We also have the Hartman v. Moore (2006) – 1st Amendment – Retaliatory Police Arrests
Retaliatory Prosecution Claims Against Government Officials – 1st Amendment
We also have the Reichle v. Howards (2012) – 1st Amendment – Retaliatory Police Arrests
Retaliatory Prosecution Claims Against Government Officials – 1st Amendment
Freedom of the Press – Flyers, Newspaper, Leaflets, Peaceful Assembly – 1$t Amendment – Learn More Here
Vermont’s Top Court Weighs: Are KKK Fliers – 1st Amendment Protected Speech
We also have the Insulting letters to politician’s home are constitutionally protected, unless they are ‘true threats’ – Letters to Politicians Homes – 1st Amendment
We also have the First Amendment Encyclopedia very comprehensive – 1st Amendment
Sanctions and Attorney Fee Recovery for Bad Actors
FAM § 3027.1 – Attorney’s Fees and Sanctions For False Child Abuse Allegations – Family Code 3027.1 – Click Here
FAM § 271 – Awarding Attorney Fees– Family Code 271 Family Court Sanction Click Here
Awarding Discovery Based Sanctions in Family Law Cases – Click Here
FAM § 2030 – Bringing Fairness & Fee Recovery – Click Here
Zamos v. Stroud – District Attorney Liable for Bad Faith Action – Click Here
Malicious Use of Vexatious Litigant – Vexatious Litigant Order Reversed
Mi$Conduct – Pro$ecutorial Mi$Conduct Prosecutor$
Attorney Rule$ of Engagement – Government (A.K.A. THE PRO$UCTOR) and Public/Private Attorney
What is a Fiduciary Duty; Breach of Fiduciary Duty
The Attorney’s Sworn Oath
Malicious Prosecution / Prosecutorial Misconduct – Know What it is!
New Supreme Court Ruling – makes it easier to sue police
Possible courses of action Prosecutorial Misconduct
Misconduct by Judges & Prosecutor – Rules of Professional Conduct
Functions and Duties of the Prosecutor – Prosecution Conduct
Standards on Prosecutorial Investigations – Prosecutorial Investigations
Information On Prosecutorial Discretion
Why Judges, District Attorneys or Attorneys Must Sometimes Recuse Themselves
Fighting Discovery Abuse in Litigation – Forensic & Investigative Accounting – Click Here
Criminal Motions § 1:9 – Motion for Recusal of Prosecutor
Pen. Code, § 1424 – Recusal of Prosecutor
Removing Corrupt Judges, Prosecutors, Jurors and other Individuals & Fake Evidence from Your Case
National District Attorneys Association puts out its standards
National Prosecution Standards – NDD can be found here
The Ethical Obligations of Prosecutors in Cases Involving Postconviction Claims of Innocence
ABA – Functions and Duties of the Prosecutor – Prosecution Conduct
Prosecutor’s Duty Duty to Disclose Exculpatory Evidence Fordham Law Review PDF
Chapter 14 Disclosure of Exculpatory and Impeachment Information PDF
Mi$Conduct – Judicial Mi$Conduct Judge$
Prosecution Of Judges For Corrupt Practice$
Code of Conduct for United States Judge$
Disqualification of a Judge for Prejudice
Judicial Immunity from Civil and Criminal Liability
Recusal of Judge – CCP § 170.1 – Removal a Judge – How to Remove a Judge
l292 Disqualification of Judicial Officer – C.C.P. 170.6 Form
How to File a Complaint Against a Judge in California?
Commission on Judicial Performance – Judge Complaint Online Form
Why Judges, District Attorneys or Attorneys Must Sometimes Recuse Themselves
Removing Corrupt Judges, Prosecutors, Jurors and other Individuals & Fake Evidence from Your Case
DUE PROCESS READS>>>>>>
Due Process vs Substantive Due Process learn more HERE
Understanding Due Process – This clause caused over 200 overturns in just DNA alone Click Here
Mathews v. Eldridge – Due Process – 5th, & 14th Amendment
Mathews Test – 3 Part Test– Amdt5.4.5.4.2 Mathews Test
“Unfriending” Evidence – 5th Amendment
At the Intersection of Technology and Law
We also have the Introducing TEXT & EMAIL Digital Evidence in California Courts – 1st Amendment
so if you are interested in learning about Introducing Digital Evidence in California State Courts
click here for SCOTUS rulings
Right to Travel freely – When the Government Obstructs Your Movement – 14th Amendment & 5th Amendment
What is Probable Cause? and.. How is Probable Cause Established?
Misuse of the Warrant System – California Penal Code § 170 – Crimes Against Public Justice – 4th, 5th, & 14th Amendment
What Is Traversing a Warrant (a Franks Motion)?
Dwayne Furlow v. Jon Belmar – Police Warrant – Immunity Fail – 4th, 5th, & 14th Amendment
Obstruction of Justice and Abuse of Process
What Is Considered Obstruction of Justice in California?
Penal Code 135 PC – Destroying or Concealing Evidence
Penal Code 141 PC – Planting or Tampering with Evidence in California
Penal Code 142 PC – Peace Officer Refusing to Arrest or Receive Person Charged with Criminal Offense
Penal Code 182 PC – “Criminal Conspiracy” Laws & Penalties
Penal Code 664 PC – “Attempted Crimes” in California
Penal Code 32 PC – Accessory After the Fact
Penal Code 31 PC – Aiding and Abetting Laws
What is Abuse of Process?
What is a Due Process Violation? – 4th Amendment & 14th Amendment
What’s the Difference between Abuse of Process, Malicious Prosecution and False Arrest?
Defeating Extortion and Abuse of Process in All Their Ugly Disguises
The Use and Abuse of Power by Prosecutors (Justice for All)
ARE PEOPLE LYING ON YOU?
CAN YOU PROVE IT? IF YES…. THEN YOU ARE IN LUCK!
Penal Code 118 PC – California Penalty of “Perjury” Law
Federal Perjury – Definition by Law
Penal Code 132 PC – Offering False Evidence
Penal Code 134 PC – Preparing False Evidence
Penal Code 118.1 PC – Police Officer$ Filing False Report$
Spencer v. Peters– Police Fabrication of Evidence – 14th Amendment
Penal Code 148.5 PC – Making a False Police Report in California
Penal Code 115 PC – Filing a False Document in California
Misconduct by Government Know Your Rights Click Here
Under 42 U.S.C. $ection 1983 – Recoverable Damage$
42 U.S. Code § 1983 – Civil Action for Deprivation of Right$
18 U.S. Code § 242 – Deprivation of Right$ Under Color of Law
18 U.S. Code § 241 – Conspiracy against Right$
Section 1983 Lawsuit – How to Bring a Civil Rights Claim
Suing for Misconduct – Know More of Your Right$
Police Misconduct in California – How to Bring a Lawsuit
How to File a complaint of Police Misconduct? (Tort Claim Forms here as well)
Deprivation of Rights – Under Color of the Law
What is Sua Sponte and How is it Used in a California Court?
Removing Corrupt Judges, Prosecutors, Jurors
and other Individuals & Fake Evidence from Your Case
Anti-SLAPP Law in California
Freedom of Assembly – Peaceful Assembly – 1st Amendment Right
How to Recover “Punitive Damages” in a California Personal Injury Case
Pro Se Forms and Forms Information(Tort Claim Forms here as well)
What is Tort?
Tort Claims Form
File Government Claim for Eligible Compensation
Complete and submit the Government Claim Form, including the required $25 filing fee or Fee Waiver Request, and supporting documents, to the GCP.
See Information Guides and Resources below for more information.
Tort Claims – Claim for Damage, Injury, or Death (see below)
Federal – Federal SF-95 Tort Claim Form Tort Claim online here or download it here or here from us
California – California Tort Claims Act – California Tort Claim Form Here or here from us
Complaint for Violation of Civil Rights (Non-Prisoner Complaint) and also UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT PDF
Taken from the UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE EASTERN DISTRICT OF CALIFORNIA Forms source
WRITS and WRIT Types in the United States
How do I submit a request for information?
To submit a request send the request via mail, fax, or email to the agency. Some agencies list specific departments or people whose job it is to respond to PRA requests, so check their websites or call them for further info. Always keep a copy of your request so that you can show what you submitted and when.
Templates for Sample Requests
Incident Based Request: Use this template if you want records related to a particular incident, like the investigative record for a specific police shooting, an arrest where you believe an officer may have been found to have filed a false report, or to find out whether complaint that an officer committed sexual assault was sustained.
ACLU Download Word document | ACLU Download PDF
or from us Download Word document | or from us Download PDF
Officer Based Request: Use this template if you want to find any public records of misconduct related to a particular officer or if he or she has been involved in past serious uses of force.
ACLU Download Word document | ACLU Download PDF
or from us Download Word document | or from us Download PDF
The First Amendment Coalition also has some useful information to help explain the PRA process.
Sample Letter | SB 1421 & SB 16 Records
Appealing/Contesting Case/Order/Judgment/Charge/ Suppressing Evidence
First Things First: What Can Be Appealed and What it Takes to Get Started – Click Here
Options to Appealing– Fighting A Judgment Without Filing An Appeal Settlement Or Mediation
Cal. Code Civ. Proc. § 1008 Motion to Reconsider
Penal Code 1385 – Dismissal of the Action for Want of Prosecution or Otherwise
Penal Code 1538.5 – Motion To Suppress Evidence in a California Criminal Case
CACI No. 1501 – Wrongful Use of Civil Proceedings
Penal Code “995 Motions” in California – Motion to Dismiss
WIC § 700.1 – If Court Grants Motion to Suppress as Evidence
Suppression Of Exculpatory Evidence / Presentation Of False Or Misleading Evidence – Click Here
Notice of Appeal — Felony (Defendant) (CR-120) 1237, 1237.5, 1538.5(m) – Click Here
California Motions in Limine – What is a Motion in Limine?
Petition for a Writ of Mandate or Writ of Mandamus (learn more…)
PC 1385 – Dismissal of the Action for Want of Prosecution or Otherwise
Retrieving Evidence / Internal Investigation Case
Conviction Integrity Unit (“CIU”) of the Orange County District Attorney OCDA – Click Here
Fighting Discovery Abuse in Litigation – Forensic & Investigative Accounting – Click Here
Orange County / LA County Data, BodyCam, Police Report, Incident Reports,
and all other available known requests for data below:
SEARCH SB-1421 SB-16 Incidents of LA County, Oakland
California Senate Bill 16 (SB 16) – 2023-2024 – Peace officers: Release of Records
APPLICATION TO EXAMINE LOCAL ARREST RECORD UNDER CPC 13321 Click Here
Learn About Policy 814: Discovery Requests OCDA Office – Click Here
Request for Proof In-Custody Form Click Here
Request for Clearance Letter Form Click Here
Application to Obtain Copy of State Summary of Criminal HistoryForm Click Here
Request Authorization Form Release of Case Information – Click Here
Texts / Emails AS EVIDENCE: Authenticating Texts for California Courts
Can I Use Text Messages in My California Divorce?
Two-Steps And Voila: How To Authenticate Text Messages
How Your Texts Can Be Used As Evidence?
California Supreme Court Rules:
Text Messages Sent on Private Government Employees Lines
Subject to Open Records Requests
case law: City of San Jose v. Superior Court – Releasing Private Text/Phone Records of Government Employees
Public Records Practices After the San Jose Decision
The Decision Briefing Merits After the San Jose Decision
Rules of Admissibility – Evidence Admissibility
Confrontation Clause – Sixth Amendment
Exceptions To The Hearsay Rule – Confronting Evidence
Prosecutor’s Obligation to Disclose Exculpatory Evidence
Successful Brady/Napue Cases – Suppression of Evidence
Cases Remanded or Hearing Granted Based on Brady/Napue Claims
Unsuccessful But Instructive Brady/Napue Cases
ABA – Functions and Duties of the Prosecutor – Prosecution Conduct
Frivolous, Meritless or Malicious Prosecution – fiduciary duty
Section 832.7 – Peace officer or custodial officer personnel records
Senate Bill No. 1421 – California Public Records Act
Assembly Bill 748 Makes Video Evidence Captured by Police Agencies Subject to Disclosure as Public Records
SB 2, Creating Police Decertification Process and Expanding Civil Liability Exposure
The Right To Know: How To Fulfill The Public’s Right Of Access To Police Records
How Access to California Police Records
Los Angeles County Sheriff’s Department SB-1421 Records
SB1421 – Form Access to California Police Records
California Statewide CPRA Requests Submit a CPRA Request
Electronic Audio Recording Request of OC Court Hearings
CPRA Public Records Act Data Request – Click Here
Here is the Public Records Service Act Portal for all of CALIFORNIA Click Here
Police BodyCam Footage Release
Cleaning Up Your Record
Tossing Out an Inferior Judgement – When the Judge Steps on Due Process – California Constitution Article VI – Judicial Section 13
Penal Code 851.8 PC – Certificate of Factual Innocence in California
Petition to Seal and Destroy Adult Arrest Records – Download the PC 851.8 BCIA 8270 Form Here
SB 393: The Consumer Arrest Record Equity Act – 851.87 – 851.92 & 1000.4 – 11105 – CARE ACT
Expungement California – How to Clear Criminal Records Under Penal Code 1203.4 PC
How to Vacate a Criminal Conviction in California – Penal Code 1473.7 PC
Seal & Destroy a Criminal Record
Cleaning Up Your Criminal Record in California (focus OC County)
Governor Pardons –What Does A Governor’s Pardon Do
How to Get a Sentence Commuted (Executive Clemency) in California
How to Reduce a Felony to a Misdemeanor – Penal Code 17b PC Motion
PARENT CASE LAW
RELATIONSHIP WITH YOUR CHILDREN &
YOUR CONSTITUIONAL RIGHT$ + RULING$
YOU CANNOT GET BACK TIME BUT YOU CAN HIT THOSE IMMORAL NON CIVIC MINDED PUNKS WHERE THEY WILL FEEL YOU = THEIR BANK
Family Law Appeal – Learn about appealing a Family Court Decision Here
9.3 Section 1983 Claim Against Defendant as (Individuals) — 14th Amendment this CODE PROTECT$ all US CITIZEN$
Amdt5.4.5.6.2 – Parental and Children’s Rights“> – 5th Amendment this CODE PROTECT$ all US CITIZEN$
9.32 – Interference with Parent / Child Relationship – 14th Amendment this CODE PROTECT$ all US CITIZEN$
California Civil Code Section 52.1
Interference with exercise or enjoyment of individual rights
Parent’s Rights & Children’s Bill of Rights
SCOTUS RULINGS FOR YOUR PARENT RIGHTS
SEARCH of our site for all articles relating for PARENTS RIGHTS Help!
Child’s Best Interest in Custody Cases
Are You From Out of State (California)? FL-105 GC-120(A)
Declaration Under Uniform Child Custody Jurisdiction and Enforcement Act (UCCJEA)
Learn More:Family Law Appeal
Necessity Defense in Criminal Cases
Can You Transfer Your Case to Another County or State With Family Law? – Challenges to Jurisdiction
Venue in Family Law Proceedings
GRANDPARENT CASE LAW
Do Grandparents Have Visitation Rights? If there is an Established Relationship then Yes
Third “PRESUMED PARENT” Family Code 7612(C) – Requires Established Relationship Required
Cal State Bar PDF to read about Three Parent Law –
The State Bar of California family law news issue4 2017 vol. 39, no. 4.pdf
Distinguishing Request for Custody from Request for Visitation
Troxel v. Granville, 530 U.S. 57 (2000) – Grandparents – 14th Amendment
S.F. Human Servs. Agency v. Christine C. (In re Caden C.)
9.32 Particular Rights – Fourteenth Amendment – Interference with Parent / Child Relationship
Child’s Best Interest in Custody Cases
When is a Joinder in a Family Law Case Appropriate? – Reason for Joinder
Joinder In Family Law Cases – CRC Rule 5.24
GrandParents Rights To Visit
Family Law Packet OC Resource Center
Family Law Packet SB Resource Center
Motion to vacate an adverse judgment
Mandatory Joinder vs Permissive Joinder – Compulsory vs Dismissive Joinder
When is a Joinder in a Family Law Case Appropriate?
Kyle O. v. Donald R. (2000) 85 Cal.App.4th 848
Punsly v. Ho (2001) 87 Cal.App.4th 1099
Zauseta v. Zauseta (2002) 102 Cal.App.4th 1242
S.F. Human Servs. Agency v. Christine C. (In re Caden C.)
Family Treatment Court Best Practice Standards
Download Here this Recommended Citation
 Epic Criminal / Civil Right$ SCOTUS Help – Click Here
Epic Criminal / Civil Right$ SCOTUS Help – Click Here
 Epic Parents SCOTUS Ruling – Parental Right$ Help – Click Here
Epic Parents SCOTUS Ruling – Parental Right$ Help – Click Here
 Judge’s & Prosecutor’s Jurisdiction– SCOTUS RULINGS on
Judge’s & Prosecutor’s Jurisdiction– SCOTUS RULINGS on
 Prosecutional Misconduct – SCOTUS Rulings re: Prosecutors
Prosecutional Misconduct – SCOTUS Rulings re: Prosecutors
Please take time to learn new UPCOMING
The PROPOSED Parental Rights Amendment
to the US CONSTITUTION Click Here to visit their site
The proposed Parental Rights Amendment will specifically add parental rights in the text of the U.S. Constitution, protecting these rights for both current and future generations.
The Parental Rights Amendment is currently in the U.S. Senate, and is being introduced in the U.S. House.