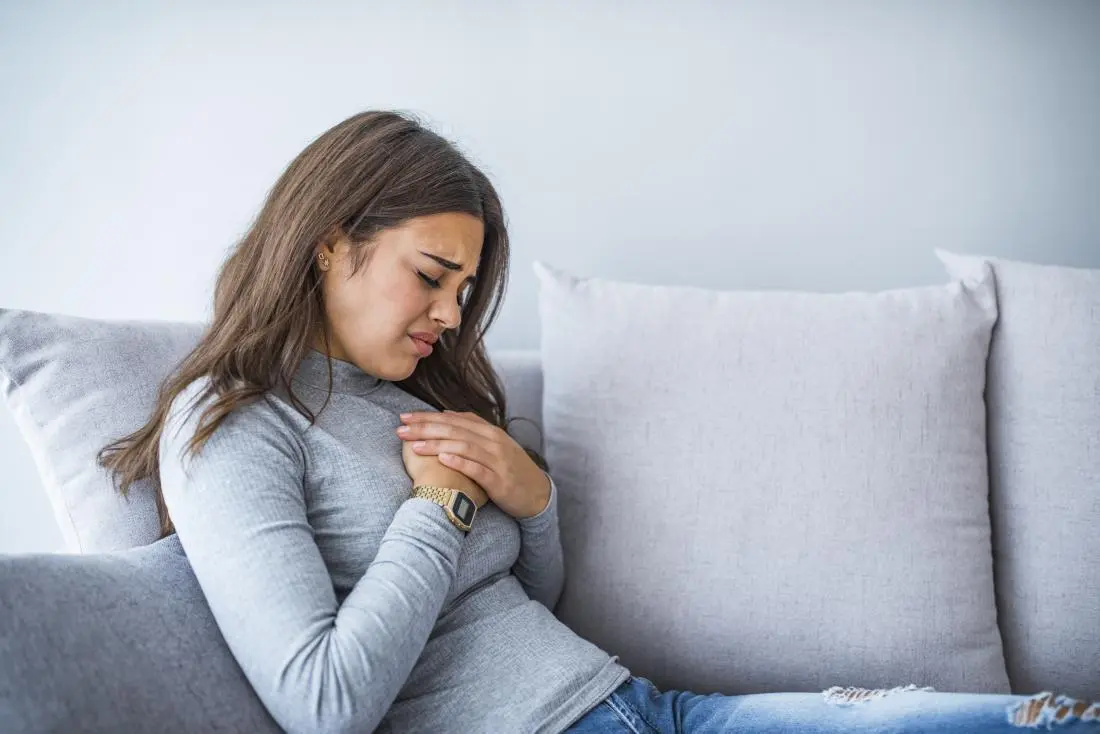
What is the difference between heart attack and stroke?
How are a stroke and heart attack different?
stroke vs. heart attack
Heart attack and stroke are both potentially life-threatening conditions that require emergency medical care.
Both can cause permanent damage to important organs, affecting quality of life and even causing death.
Though heart attack and stroke have several factors in common, their symptoms, treatments, and recovery processes will differ.
In this article, we discuss these differences. Knowing them is vital for identifying and managing stroke and heart attack.
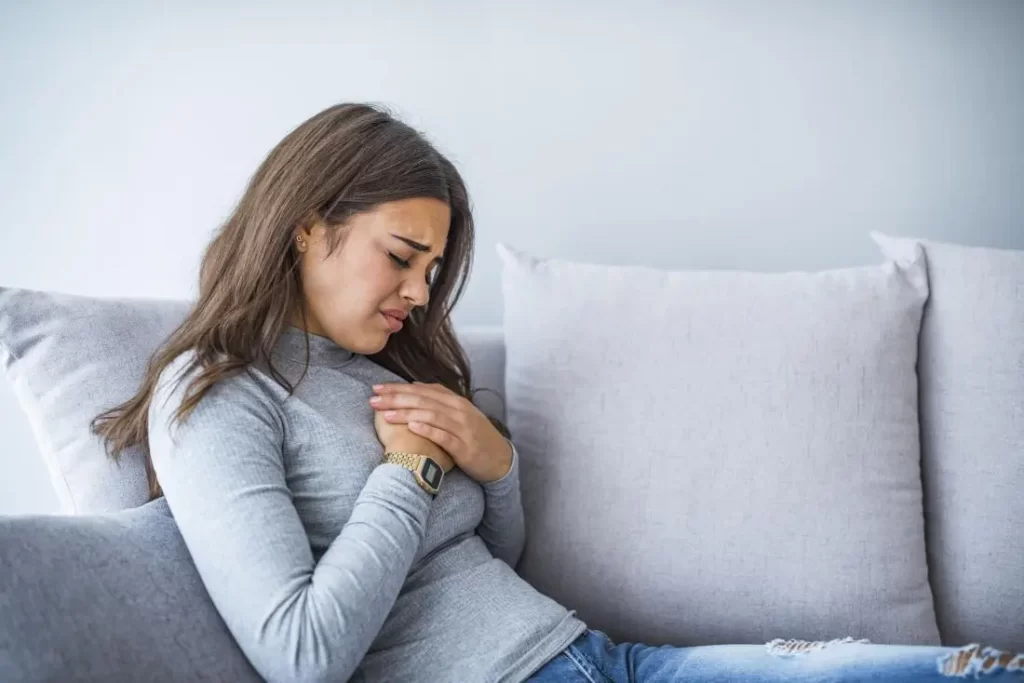

Learning the warning signs of heart attack and stroke is important. Seek emergency medical care immediately if any symptoms appear.
Chest pain is one of most recognizable symptoms of a heart attack. While it is the most common symptom, many people who experience a heart attack have little to no chest pain.
These people may not realize that they are having a heart attack, and they may not seek medical care as quickly as needed.
Other symptoms that may indicate a heart attack include:
- a feeling of pressure, fullness, or squeezing in the chest
- pain in the jaw, neck, arms, back, or stomach
- feeling short of breath
- lightheadedness or fainting
- cold sweats
- nausea or vomiting
Women are more likelyTrusted Source than men to experience nausea, vomiting, shortness of breath, and jaw pain during a heart attack.
Anyone who experiences these symptoms should seek care immediately.
There are two types of stroke: ischemic and hemorrhagic. Most people who have a stroke have an ischemic stroke. A blood clot in one of the brain’s blood vessels usually causes this.
A blockage or plaque does not cause hemorrhagic stroke. Instead, a burst artery can lead to this type of stroke.
A stroke can rapidly damage the brain, leading to permanent disability or death. Stroke symptoms begin quickly, often with no warning.
They may include:
- drooping on one side of the face, or being unable to move one side of the face
- weakness or numbness in one arm, in which the person may be unable to raise both arms evenly out to the side
- slurred speech or difficulty talking, during which the person may not be able to repeat simple words or sentences clearly
- vision loss in one eye
- loss of balance, frequent falling, or dizziness
A transient ischemic attack (TIA), or mini-stroke, produces symptoms very similar to a stroke, but it only lasts for a few minutes. A TIA does not permanently damage the brain.
However, do not ignore them. Around 4 in 10 people who have a TIA will go on to have a stroke.
Anyone who experiences stroke symptoms should see a doctor immediately, even if they pass quickly.
Atherosclerosis causes a buildup of plaque, a substance that restricts and hardens the blood vessels. This disease causes the majority of strokes and heart attacks.
Over time, the plaque can harden and break off, causing a blood clot to form. The clot can block the blood vessel and starve vital organs of oxygen.
During most heart attacks, a clot blocks a coronary artery, which is one of the heart’s blood vessels. Therefore, part of the heart muscle rapidly loses its blood supply and may incur permanent damage.
Similarly, most strokes are due to the blockage of a blood vessel somewhere in the brain. The clot robs the brain of its vital blood supply and can lead to brain damage.
Blocked arteries and blood clots can cause both heart attacks and strokes. So, their treatment may be similar in several ways.
In both conditions, a doctor may prescribe a person clot-busting medicines in the hospital. These medications are called thrombolytics, and they help dissolve the blood clot and restore blood flow to the affected organ.
Doctors usually need to administer thrombolytics as soon as possible after the symptoms begin, or at least within a few hours of onset.
Through an endovascular procedure, a specialist may also physically remove any blood clots in the coronary or carotid arteries. This is a nonsurgical procedure that uses a thin tube to grip the clot and remove it.
Examples of an endovascular procedure include:
- percutaneous coronary intervention for heart attack
- mechanical thrombectomy for stroke
Not everyone would benefit from a clot-removing procedure after a stroke or heart attack. If this surgery takes place, a specialist should perform it as soon as possible after symptoms become apparent.
After stroke or heart attack, doctors tend to prescribe certain medicines. These drugs can help by:
- reducing future plaque buildup in the arteries
- lowering blood pressure or cholesterol
- reducing blood clots
Taking these medicines long-term may help a person prevent another heart attack or stroke.
Though some heart attack and stroke medicines may overlap, different treatments can help each condition. A doctor will base the particular medications they prescribe on a person’s medical history.
People who have had a heart attack might receive specific medicines that can help reduce stress on the heart, prevent further heart damage, and relieve chest pain.
People who have diabetes have higher risk of stroke, so a doctor might choose to prescribe medications to help regulate blood sugar to control this increased risk.
Many cases of stroke and heart attack are due to plaque buildup inside the arteries. For this reason, either condition may involve certain lifestyle changes, including:
- following a heart-healthy diet
- getting regular exercise
- quitting smoking
- maintaining a healthy weight
These changes can help the body recover from a stroke or heart attack and reduce the risk of having another, as well as promote general wellness.
The most important factor of good recovery from a heart attack or stroke is getting treatment as soon as possible.
Recovery from many heart attacks and strokes requires some kind of rehabilitation or physical therapy. The type of therapy and the goals of the treatment are usually quite different between the two conditions.
Therapy following a heart attack
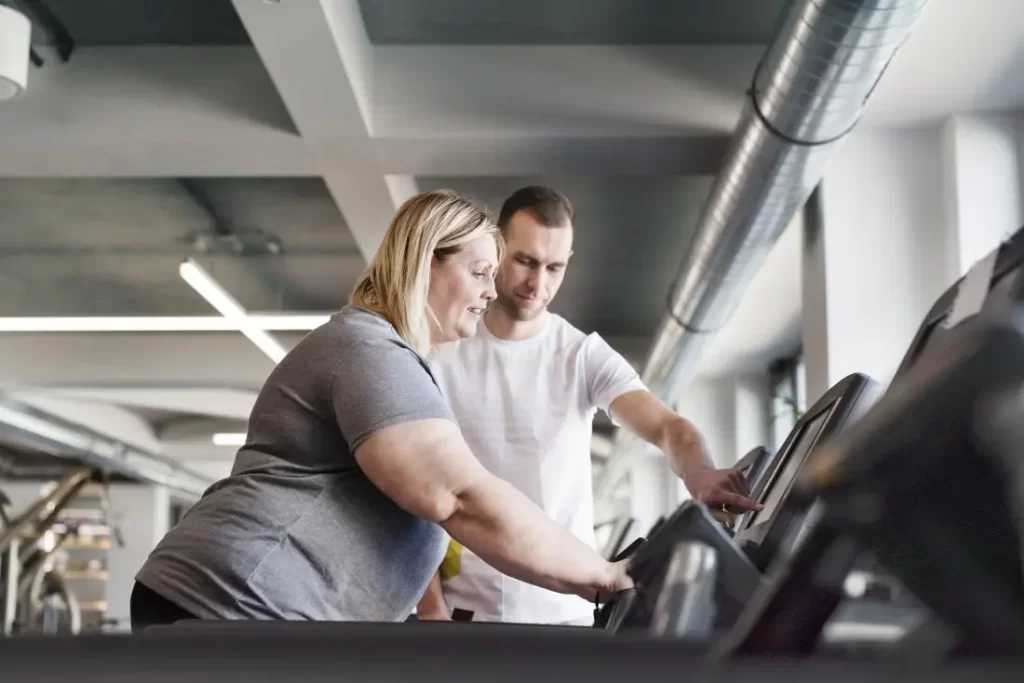

After a heart attack, a person may require cardiac rehabilitation.
This is specialized therapy designed to improve heart health. A doctor supervises this treatment.
Cardiac rehabilitation usually includes:
- Exercising: A cardiac rehabilitation specialist guides a person through exercise that is heart-healthy and safe for them to do.
- Receiving information about living a heart-healthy life: This includes adopting a healthful diet, quitting smoking, and managing heart attack risk factors.
- Reducing stress: Finding ways to manage stress can help improve heart health.
Therapy following a stroke
Therapy after a stroke is quite different from rehabilitation after a heart attack.
If a person experiences brain damage during a stroke, therapy might include a variety of exercises to help a person regain physical and psychological functions they may have lost.
Most strokes cause one of the following disabilities, which may be temporary or permanent:
- problems with movement or paralysis in certain areas of the body
- trouble swallowing
- changes in behavior or emotions
- problems with thinking and memory
- trouble talking or understanding other people
- uncontrolled urine leakage or bowel movements
- changes to vision, taste, or smell
Heart attack and stroke are similar in many ways, but each requires different care and follow-up.
Having a heart-healthy lifestyle and regularly visiting the doctor can help minimize the risk of these life-threatening conditions. However, it cannot prevent them entirely.
Q: How are heart attack and stroke different from heart failure?
A: Heart attack and stroke are both acute conditions, while heart failure is a chronic condition. Heart attack occurs when blood flow to part of the heart is blocked, causing an insult to the heart muscle. Stroke, on the other hand, occurs when blood flow from part of the brain is cut off due to a blocked or ruptured blood vessel.
Medical professionals consider heart failure a progressive and chronic condition. With heart failure, the heart cannot pump enough blood effectively to meet the demands of the body.
Gerhard Whitworth, RNTrusted Source Answers represent the opinions of our medical experts. All content is strictly informational and should not be considered medical advice.

